Page 144 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 144
30 Woven Composites 133
experienced by 3D carbodepoxy composites reinforced with an orthogonal or
interlocked woven structure (Billaut and Rousell, 1995). The amount of damage
suffered by an aerospace-grade carbodepoxy laminate is shown for comparison. It is
seen the amount of impact damage experienced by the 3D woven composites is lower
than the 2D laminate. The outstanding damage resistance of 3D woven composites is
due to their high delamination resistance. The interlaminar toughening mechanisms
described in the previous section, namely debonding, fracture, pull-out and, in
particular, crack bridging of the z-binders impede the spread of delaminations from the
impact site. The superior impact damage resistance of 3D woven composites usually
results in higher post-impact mechanical properties than for 2D laminates (Arendts et
al., 1993; Brandt et al., 1996; James and Howlett, 1997; Susuki and Takatoya, 1997;
Voss et al., 1993). For example, in Figure 5.26 it is shown that the post-impact flexural
and compressive strengths of 3D woven composites are significantly higher than for 2D
laminates (Arendts et al., 1993; Voss et al., 1993).
4r
Mode I Mode I1
2D Laminate3D Composite 2D Laminate 3D Composite
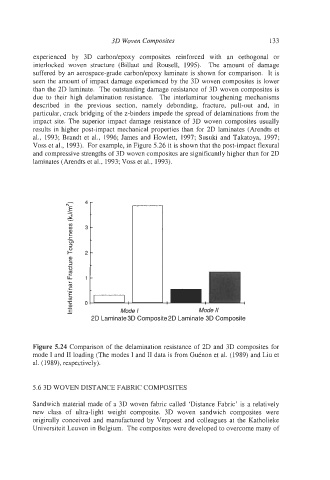
Figure 5.24 Comparison of the delamination resistance of 2D and 3D composites for
mode I and I1 loading (The modes I and I1 data is from GuCnon et al. (1989) and Liu et
al. (1989), respectively).
5.6 3D WOVEN DISTANCE FABRIC COMPOSITES
Sandwich material made of a 3D woven fabric called ‘Distance Fabric’ is a relatively
new class of ultra-light weight composite. 3D woven sandwich composites were
originally conceived and manufactured by Verpoest and colleagues at the Katholieke
Universiteit Leuven in Belgium. The composites were developed to overcome many of