Page 138 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 138
30 Woven Composites 127
cases the flexural properties of a 3D woven composite are lower than for an equivalent
2D laminate. In the worst reported case, Guess and Reedy (1985) found that the
flexural modulus and strength of a 3D Kevlar/epoxy composite was respectively 20%
and 30% lower than a 2D laminate. The reduced flexural properties are due to the
crimping and increased misalignment of the tows by the z-binders.
5.3.4 Interlaminar Shear Properties
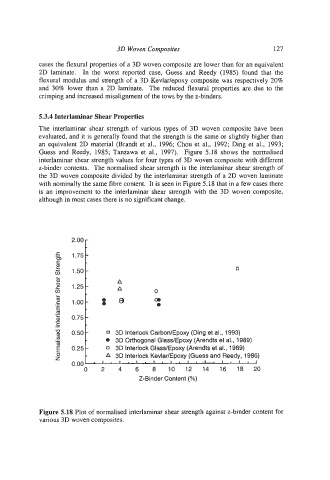
The interlaminar shear strength of various types of 3D woven composite have been
evaluated, and it is generally found that the strength is the same or slightly higher than
an equivalent 2D material (Brandt et al., 1996; Chou et al., 1992; Ding et al., 1993;
Guess and Reedy, 1985; Tanzawa et al., 1997). Figure 5.18 shows the normalised
interlaminar shear strength values for four types of 3D woven composite with different
z-binder contents. The normalised shear strength is the interlaminar shear strength of
the 3D woven composite divided by the interlaminar strength of a 2D woven laminate
with nominally the same fibre content. It is seen in Figure 5.18 that in a few cases there
is an improvement to the interlaminar shear strength with the 3D woven composite,
although in most cases there is no significant change.
L
I! m 1.251 A
A
(I)
z c.
._ c 1.00- : 8 0
E
-
0.75-
-
c
8
0.50 - 0 3D Interlock Carbon/Epoxy (Ding et al., 1993)
.- - 0 3D Orthogonal GlasdEpoxy (Arendts et ai., 1989)
v)
m 0.25 - 0 3D Interlock Glass/Epoxy (Arendts et al., 1989)
E
z * ' A 3D Interlock Kevlar/Epoxy (Guess and Reedy, 1986)
* '
'
0.00 ' I " I ' I ' I a ' I "
Figure 5.18 Plot of normalised interlaminar shear strength against z-binder content for
various 3D woven composites.