Page 134 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 134
30 Woven Composites 123
5.3.2 Compressive Properties
The compressive properties and failure mechanisms of 3D woven composites have been
investigated in great detail because of their potential application in aerospace structures.
Most attention has been given to 3D carbordepoxy composites because of their use in
aircraft, although 3D carbodbismaleimide and 3D Kevlar/epoxy have also been
examined. Most studies find that the compressive modulus of 3D woven composites is
lower than 2D prepreg tape or woven laminate with a similar fibre volume content
(Brandt et al., 1996; Guess and Reedy, 1986; Farley et al., 1992). The reduced modulus
is due to crimping and increased waviness of the load-bearing fibres caused by the z-
binders.
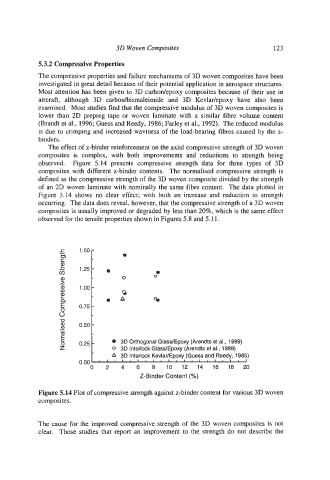
The effect of z-binder reinforcement on the axial compressive strength of 3D woven
composites is complex, with both improvements and reductions to strength being
observed. Figure 5.14 presents compressive strength data for three types of 3D
composites with different z-binder contents. The normalised compressive strength is
defined as the compressive strength of the 3D woven composite divided by the strength
of an 2D woven laminate with nominally the same fibre content. The data plotted in
Figure 5.14 shows no clear effect; with both an increase and reduction to strength
occurring. The data does reveal, however, that the compressive strength of a 3D woven
composites is usually improved or degraded by less than 20%, which is the same effect
observed for the tensile properties shown in Figures 5.8 and 5.1 1.
-
1.50
1.25 -
0
0 0
-
1.00
-
0.75
-
0.50
- 3D Orthogonal GlasdEpoxy (Arendts et al., 1989)
0.25
0 3D Interlock Glass/Epoxy (Arendts et al., 1989)
A 3D Interlock KevlarlEpoxy (Guess and Reedy, 1985)
0.00' - I . ' ' ' ' I * ' * I - ' a ' ' ' ' '
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Z-Binder Content (%)
Figure 5.14 Plot of compressive strength against z-binder content for various 3D woven
composites.
The cause for the improved compressive strength of the 3D woven composites is not
clear. Those studies that report an improvement to the strength do not describe the