Page 31 - A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Energy Systems
P. 31
Chapter 2 • Solar Power Development in China 25
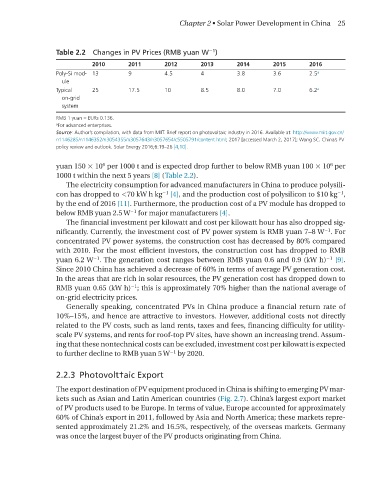
Table 2.2 Changes in PV Prices (RMB yuan W )
−1
2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
Poly-Si mod- 13 9 4.5 4 3.8 3.6 2.5 a
ule
Typical 25 17.5 10 8.5 8.0 7.0 6.2 a
on-grid
system
RMB 1 yuan = EURs 0.136.
a For advanced enterprises.
Source: Author’s compilation, with data from MIIT. Brief report on photovoltaic industry in 2016. Available at: http://www.miit.gov.cn/
n1146285/n1146352/n3054355/n3057643/n3057654/c5505791/content.html; 2017 [accessed March 2, 2017]; Wang SC. China’s PV
policy review and outlook. Solar Energy 2016;6:19–26 [4,10].
6
yuan 150 × 10 per 1000 t and is expected drop further to below rMB yuan 100 × 10 per
6
1000 t within the next 5 years [8] (Table 2.2).
The electricity consumption for advanced manufacturers in China to produce polysili-
con has dropped to <70 kW h kg [4], and the production cost of polysilicon to $10 kg ,
−1
−1
by the end of 2016 [11]. Furthermore, the production cost of a PV module has dropped to
below rMB yuan 2.5 W for major manufacturers [4].
−1
The financial investment per kilowatt and cost per kilowatt hour has also dropped sig-
nificantly. Currently, the investment cost of PV power system is rMB yuan 7–8 W . For
−1
concentrated PV power systems, the construction cost has decreased by 80% compared
with 2010. For the most efficient investors, the construction cost has dropped to rMB
yuan 6.2 W . The generation cost ranges between rMB yuan 0.6 and 0.9 (kW h) [9].
−1
−1
Since 2010 China has achieved a decrease of 60% in terms of average PV generation cost.
In the areas that are rich in solar resources, the PV generation cost has dropped down to
rMB yuan 0.65 (kW h) ; this is approximately 70% higher than the national average of
−1
on-grid electricity prices.
Generally speaking, concentrated PVs in China produce a financial return rate of
10%–15%, and hence are attractive to investors. However, additional costs not directly
related to the PV costs, such as land rents, taxes and fees, financing difficulty for utility-
scale PV systems, and rents for roof-top PV sites, have shown an increasing trend. Assum-
ing that these nontechnical costs can be excluded, investment cost per kilowatt is expected
−1
to further decline to rMB yuan 5 W by 2020.
2.2.3 Photovolt†aic Export
The export destination of PV equipment produced in China is shifting to emerging PV mar-
kets such as Asian and latin American countries (Fig. 2.7). China’s largest export market
of PV products used to be Europe. In terms of value, Europe accounted for approximately
60% of China’s export in 2011, followed by Asia and North America; these markets repre-
sented approximately 21.2% and 16.5%, respectively, of the overseas markets. Germany
was once the largest buyer of the PV products originating from China.