Page 332 - A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Energy Systems
P. 332
Chapter 16 • Small-Scale PV Systems Used in Domestic Applications 337
open-circuit voltage (V oC ), the short circuit current (I SC ), the voltage and the current at the
MPP (V MPP and I MPP ), and the maximum power itself (P Max ). It is the primary aim of any
converter system to operate the PV cell at its MPP in any condition for maximum utiliza-
tion (higher efficiency). It is important to note that such an ideal power point tracking
curve is valid for either a single uniformly illuminated cell or a set of matched cells with
identical radiance.
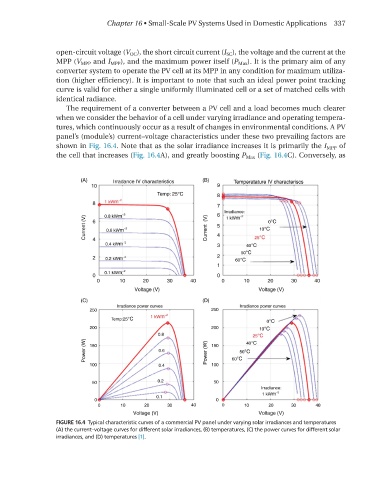
The requirement of a converter between a PV cell and a load becomes much clearer
when we consider the behavior of a cell under varying irradiance and operating tempera-
tures, which continuously occur as a result of changes in environmental conditions. A PV
panel’s (module’s) current–voltage characteristics under these two prevailing factors are
shown in Fig. 16.4. Note that as the solar irradiance increases it is primarily the I MPP of
the cell that increases (Fig. 16.4A), and greatly boosting P Max (Fig. 16.4C). Conversely, as
FIGURE 16.4 Typical characteristic curves of a commercial PV panel under varying solar irradiances and temperatures
(A) the current–voltage curves for different solar irradiances, (B) temperatures, (C) the power curves for different solar
irradiances, and (D) temperatures [1].