Page 213 - A First Course In Stochastic Models
P. 213
206 MARKOV CHAINS AND QUEUES
0, L • • • • • • c − L, L
i 1 , i 2 + 1
•
•
2
• l 2 (i + 1)m 2
l 1 l 1
0, i 2
i 1 − 1, i 2 i 1 , i 2 i 1 + 1, i 2
i 1 m 1 (i 1 + 1)m 1
•
l 2 i 2 m 2
•
•
i 1 , i 2 − 1
0, 0 • • • • • • c , 0
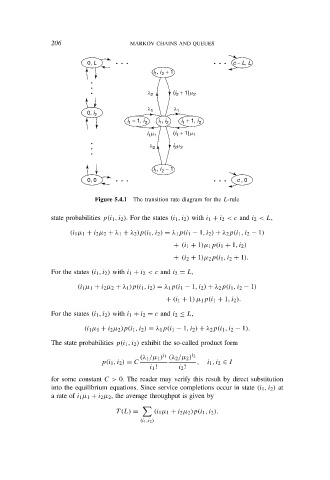
Figure 5.4.1 The transition rate diagram for the L-rule
state probabilities p(i 1 , i 2 ). For the states (i 1 , i 2 ) with i 1 + i 2 < c and i 2 < L,
(i 1 µ 1 + i 2 µ 2 + λ 1 + λ 2 )p(i 1 , i 2 ) = λ 1 p(i 1 − 1, i 2 ) + λ 2 p(i 1 , i 2 − 1)
+ (i 1 + 1)µ 1 p(i 1 + 1, i 2 )
+ (i 2 + 1)µ 2 p(i 1 , i 2 + 1).
For the states (i 1 , i 2 ) with i 1 + i 2 < c and i 2 = L,
(i 1 µ 1 + i 2 µ 2 + λ 1 )p(i 1 , i 2 ) = λ 1 p(i 1 − 1, i 2 ) + λ 2 p(i 1 , i 2 − 1)
+ (i 1 + 1) µ 1 p(i 1 + 1, i 2 ).
For the states (i 1 , i 2 ) with i 1 + i 2 = c and i 2 ≤ L,
(i 1 µ 1 + i 2 µ 2 )p(i 1 , i 2 ) = λ 1 p(i 1 − 1, i 2 ) + λ 2 p(i 1 , i 2 − 1).
The state probabilities p(i 1 , i 2 ) exhibit the so-called product form
(λ 1 /µ 1 ) (λ 2 /µ 2 ) i 2
i 1
p(i 1 , i 2 ) = C , i 1 , i 2 ∈ I
i 1 ! i 2 !
for some constant C > 0. The reader may verify this result by direct substitution
into the equilibrium equations. Since service completions occur in state (i 1 , i 2 ) at
a rate of i 1 µ 1 + i 2 µ 2 , the average throughput is given by
T (L) = (i 1 µ 1 + i 2 µ 2 )p(i 1 , i 2 ).
(i 1 ,i 2 )