Page 136 - [B._MURPHY,_C._MURPHY,_B._HATHAWAY]_A_working_meth
P. 136
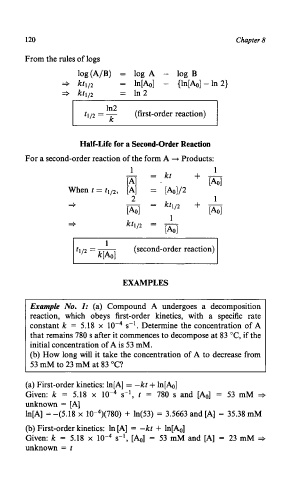
120 Chapter 8
From the rules of logs
log(A/B) = log A - log B
* kt112 = ln[Ao] - {In[&] -In 2)
* kt112 = In 2
ln2
t1p = (first-order reaction)
Half-Life for a Second-Order Reaction
For a second-order reaction of the form A -, Products:
1 1
- = kt +-
[A1 [A01
When t = t112, [A] = [&]/2
2 1
*
(second-order reaction)
EXAMPLES
Example No. I: (a) Compound A undergoes a decomposition
reaction, which obeys first-order kinetics, with a specific rate
constant k = 5.18 x s-l. Determine the concentration of A
that remains 780 s after it commences to decompose at 83 "C, if the
initial concentration of A is 53 mM.
(b) How long will it take the concentration of A to decrease from
53 mM to 23 mM at 83 "C?
(a) First-order kinetics: ln[A] = -kt + In[&]
Given: k = 5.18 x s-l, t = 780 s and [Ao] = 53 mM +
unknown = [A]
ln[A] = -(5.18 x 10-4)(780) + ln(53) = 3.5663 and [A] = 35.38 mM
(b) First-order kinetics: In [A] = -kt + ln[Ao]
Given: k = 5.18 x s-l, [Ao] = 53 mM and [A] = 23 mM =+
unknown = t