Page 96 - [B._MURPHY,_C._MURPHY,_B._HATHAWAY]_A_working_meth
P. 96
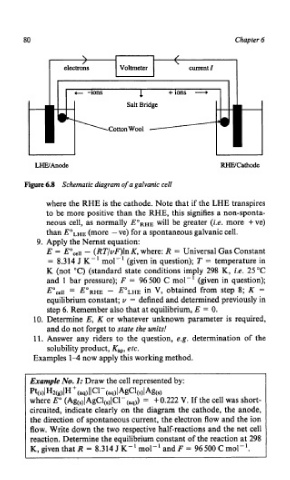
80 Chapter 6
\ /
\
Voltmeter current I
1 +ions -.+
Salt Bridge
CottonWool
WAnodt WCathode
Figure 6.8 Schematic diagram of a galvanic cell
where the RHE is the cathode. Note that if the LHE transpires
to be more positive than the RHE, this signifies a non-sponta-
neous cell, as normally EoRHE will be greater (i.e. more +ve)
than EoLHE (more - ve) for a spontaneous galvanic cell.
9. Apply the Nernst equation:
E = Eocell - (RT/uF)ln K, where: R = Universal Gas Constant
= 8.314 J K-' mol-' (given in question); T = temperature in
K (not "C) (standard state conditions imply 298 K, i.e. 25°C
and 1 bar pressure); F = 96 500 C mol-' (given in question);
Eoce.l = EORHE - EoLHE in V, obtained from step 8; K =
equilibrium constant; u = defined and determined previously in
step 6. Remember also that at equilibrium, E = 0.
10. Determine E, K or whatever unknown parameter is required,
and do not forget to state the units!
11. Answer any riders to the question, e.g. determination of the
solubility product, Ksp, etc.
Examples 1-4 now apply this working method.
1 Example No. I: Draw the cell represented by:
P~(~)IHz(~)IH+(~~)IIC~-(~~)IA~C~(~)IA~(~)
where E" (Ag(s)(AgCl(s)ICl-(aq)) = +0.222 V. If the cell was short-
circuited, indicate clearly on the diagram the cathode, the anode,
the direction of spontaneous current, the electron flow and the ion
flow. Write down the two respective half-reactions and the net cell
reaction. Determine the equilibrium constant of the reaction at 298
K, given that R = 8.314 J K-' mol-' and F = 96 500 C mol-'.