Page 98 - [B._MURPHY,_C._MURPHY,_B._HATHAWAY]_A_working_meth
P. 98
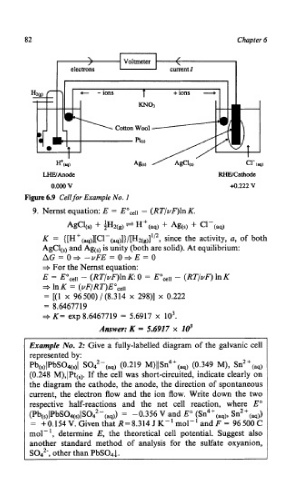
82 Chapter 6
+ /
Voltmeter
\
+ions -
T
H+(,) c1- (rq)
LHE/Anodc RIWCathode
0.000 v 4.222 v
Figure 6.9 Cell for Example No. I
9. Nernst equation: E = Eocell - (RT/vF)ln K.
AgCL,,) + $*(g) + H+(aq) + Ag(s) + Cl-(aq)
K = { [H'(aq)][Cl-(aq)])/~*(~)]''2, since the activity, u, of both
AgCl,,) and Ag(,) is unity (both are solid). At equilibrium:
AG=O+-VFE=O+E=O
+ For the Nernst equation:
E = Eocell - (RT/vF)ln K: 0 = Eocell - (RT/vF) In K
+ In K = (uF/RT)E",ll
= [(l x 96500) / (8.314 x 298)] x 0.222
= 8.6467719
=+ K= exp 8.6467719 = 5.6917 x lo3.
Answer: K = 5.6917 x Id
Example No. 2: Give a fully-labelled diagram of the galvanic cell
represented by:
Pb(,,lpbSOq,,( SO:-(aq) (0.219 M)llSn4+(,q) (0.349 M), Sn2+(,q)
(0.248 M),IPt,,). If the cell was short-circuited, indicate clearly on
the diagram the cathode, the anode, the direction of spontaneous
current, the electron flow and the ion flow. Write down the two
respective half-reactions and the net cell reaction, where E"
(Pb(,)IPbSO4(s)ISO:-(aq)) = -0.356 V and E" (Sn4+(,,), Sn2+(,,))
= +0.154V.GiventhatR=8.314JK-'mol-'andF= 96500C
mol- ', determine E, the theoretical cell potential. Suggest also
another standard method of analysis for the sulfate oxyanion,
S042-, other than PbS041.