Page 102 - [B._MURPHY,_C._MURPHY,_B._HATHAWAY]_A_working_meth
P. 102
86 Chapter 6
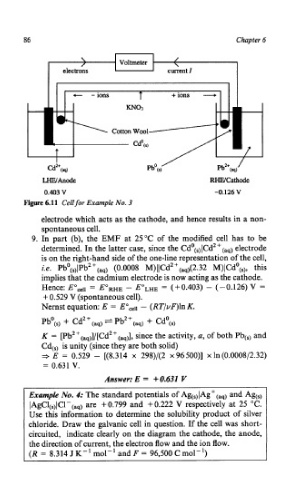
'- Voltmeter
current I
c -ions T +ions __*
mo3
Cotton Wool-
Cd0W
t
I Pb0(S) / Pb*+W /
Cd*+(a@
WAnode RWCathode
0.403 V -0.126 V
Figure 6.11 Cell for Example No. 3
electrode which acts as the cathode, and hence results in a non-
spontaneous cell.
9. In part (b), the EMF at 25°C of the modified cell has to be
determined. In the latter case, since the Cdo(s)ICd2+(aq) electrode
is on the right-hand side of the one-line representation of the cell,
i.e. Pb0(,)lPb2 + (as) (0.0008 M) I I Cd2 + (aql(2.32 M)I Cdo(s), this
implies that the cadmium electrode is now acting as the cathode.
Hence: Eocell = E"RHE - EOLHE = (+ 0.403) - (-0.126) V =
+ 0.529 V (spontaneous cell).
Nernst equation: E = Eocell - (RT/vF)ln K.
Pbo(,> + Cd2+(aq) + Pb2+(aq) + Cdo(,)
K = pb2+(aq)]/[Cd2+(aq)], since the activity, a, of both Pb(,) and
Cd,,) is unity (since they are both solid)
+ E = 0.529 - [(8.314 x 298)/(2 x 96 SOO)] x ln(0.0008/2.32)
= 0.631 V.
Answer: E = +0.631 V
Example No. 4: The standard potentials of Ag(,)lAg+(,,) and Ag(,)
IAgCl(,)lCl-(,,) are +0.799 and +0.222 V respectively at 25 "C.
Use this information to determine the solubility product of silver
chloride. Draw the galvanic cell in question. If the cell was short-
circuited, indicate clearly on the diagram the cathode, the anode,
the direction of current, the electron flow and the ion flow.
(R = 8.314 J K-' mol-' and F = 96,500 C mol-')