Page 108 - ARM 64 Bit Assembly Language
P. 108
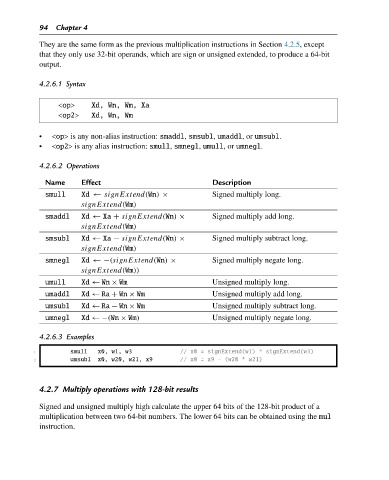
94 Chapter 4
They are the same form as the previous multiplication instructions in Section 4.2.5, except
that they only use 32-bit operands, which are sign or unsigned extended, to produce a 64-bit
output.
4.2.6.1 Syntax
<op> Xd, Wn, Wm, Xa
<op2> Xd, Wn, Wm
• <op> is any non-alias instruction: smaddl, smsubl, umaddl,or umsubl.
• <op2> is any alias instruction: smull, smnegl, umull,or umnegl.
4.2.6.2 Operations
Name Effect Description
smull Xd ← signExtend(Wn) × Signed multiply long.
signExtend(Wm)
smaddl Xd ← Xa + signExtend(Wn) × Signed multiply add long.
signExtend(Wm)
smsubl Xd ← Xa − signExtend(Wn) × Signed multiply subtract long.
signExtend(Wm)
smnegl Xd ←−(signExtend(Wn) × Signed multiply negate long.
signExtend(Wm))
umull Xd ← Wn × Wm Unsigned multiply long.
umaddl Xd ← Ra + Wn × Wm Unsigned multiply add long.
umsubl Xd ← Ra − Wn × Wm Unsigned multiply subtract long.
umnegl Xd ←−(Wn × Wm) Unsigned multiply negate long.
4.2.6.3 Examples
1 smull x0, w1, w3 // x0 = signExtend(w1) * signExtend(w3)
2 umsubl x0, w20, w21, x9 // x0 = x9 - (w20 * w21)
4.2.7 Multiply operations with 128-bit results
Signed and unsigned multiply high calculate the upper 64 bits of the 128-bit product of a
multiplication between two 64-bit numbers. The lower 64 bits can be obtained using the mul
instruction.