Page 373 - ARM 64 Bit Assembly Language
P. 373
Advanced SIMD instructions 363
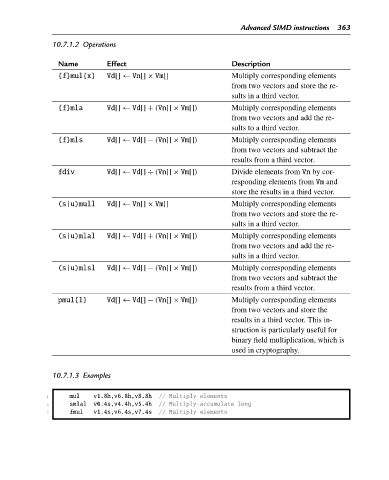
10.7.1.2 Operations
Name Effect Description
{f}mul{x} Vd[] ← Vn[] × Vm[] Multiply corresponding elements
from two vectors and store the re-
sults in a third vector.
{f}mla Vd[] ← Vd[] + (Vn[] × Vm[]) Multiply corresponding elements
from two vectors and add the re-
sults to a third vector.
{f}mls Vd[] ← Vd[] − (Vn[] × Vm[]) Multiply corresponding elements
from two vectors and subtract the
results from a third vector.
fdiv Vd[] ← Vd[] ÷ (Vn[] × Vm[]) Divide elements from Vn by cor-
responding elements from Vm and
store the results in a third vector.
(s|u)mull Vd[] ← Vn[] × Vm[] Multiply corresponding elements
from two vectors and store the re-
sults in a third vector.
(s|u)mlal Vd[] ← Vd[] + (Vn[] × Vm[]) Multiply corresponding elements
from two vectors and add the re-
sults in a third vector.
(s|u)mlsl Vd[] ← Vd[] − (Vn[] × Vm[]) Multiply corresponding elements
from two vectors and subtract the
results from a third vector.
pmul{l} Vd[] ← Vd[] − (Vn[] × Vm[]) Multiply corresponding elements
from two vectors and store the
results in a third vector. This in-
struction is particularly useful for
binary field multiplication, which is
used in cryptography.
10.7.1.3 Examples
1 mul v1.8h,v6.8h,v8.8h // Multiply elements
2 smlal v0.4s,v4.4h,v5.4h // Multiply-accumulate long
3 fmul v1.4s,v6.4s,v7.4s // Multiply elements