Page 39 - ARM 64 Bit Assembly Language
P. 39
22 Chapter 1
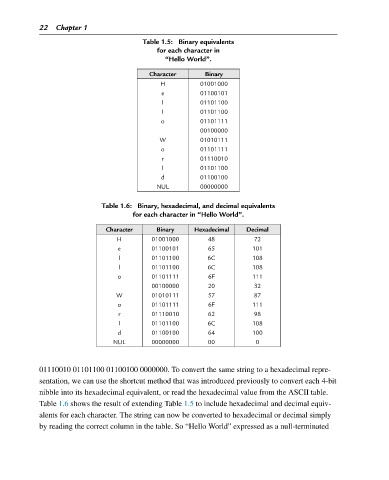
Table 1.5: Binary equivalents
for each character in
“Hello World”.
Character Binary
H 01001000
e 01100101
l 01101100
l 01101100
o 01101111
00100000
W 01010111
o 01101111
r 01110010
l 01101100
d 01100100
NUL 00000000
Table 1.6: Binary, hexadecimal, and decimal equivalents
for each character in “Hello World”.
Character Binary Hexadecimal Decimal
H 01001000 48 72
e 01100101 65 101
l 01101100 6C 108
l 01101100 6C 108
o 01101111 6F 111
00100000 20 32
W 01010111 57 87
o 01101111 6F 111
r 01110010 62 98
l 01101100 6C 108
d 01100100 64 100
NUL 00000000 00 0
01110010 01101100 01100100 0000000. To convert the same string to a hexadecimal repre-
sentation, we can use the shortcut method that was introduced previously to convert each 4-bit
nibble into its hexadecimal equivalent, or read the hexadecimal value from the ASCII table.
Table 1.6 shows the result of extending Table 1.5 to include hexadecimal and decimal equiv-
alents for each character. The string can now be converted to hexadecimal or decimal simply
by reading the correct column in the table. So “Hello World” expressed as a null-terminated