Page 196 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 196
CHAPT E R 4 The Revenue Cycle 167
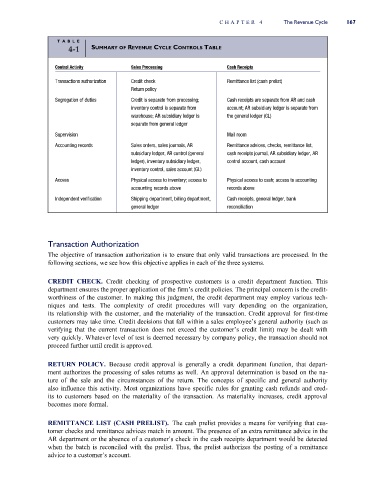
TAB L E
4-1 SUMMARY OF REVENUE CYCLE CONTROLS TABLE
Control Activity Sales Processing Cash Receipts
Transactions authorization Credit check Remittance list (cash prelist)
Return policy
Segregation of duties Credit is separate from processing; Cash receipts are separate from AR and cash
inventory control is separate from account; AR subsidiary ledger is separate from
warehouse; AR subsidiary ledger is the general ledger (GL)
separate from general ledger
Supervision Mail room
Accounting records Sales orders, sales journals, AR Remittance advices, checks, remittance list,
subsidiary ledger, AR control (general cash receipts journal, AR subsidiary ledger, AR
ledger), inventory subsidiary ledger, control account, cash account
inventory control, sales account (GL)
Access Physical access to inventory; access to Physical access to cash; access to accounting
accounting records above records above
Independent verification Shipping department, billing department, Cash receipts, general ledger, bank
general ledger reconciliation
Transaction Authorization
The objective of transaction authorization is to ensure that only valid transactions are processed. In the
following sections, we see how this objective applies in each of the three systems.
CREDIT CHECK. Credit checking of prospective customers is a credit department function. This
department ensures the proper application of the firm’s credit policies. The principal concern is the credit-
worthiness of the customer. In making this judgment, the credit department may employ various tech-
niques and tests. The complexity of credit procedures will vary depending on the organization,
its relationship with the customer, and the materiality of the transaction. Credit approval for first-time
customers may take time. Credit decisions that fall within a sales employee’s general authority (such as
verifying that the current transaction does not exceed the customer’s credit limit) may be dealt with
very quickly. Whatever level of test is deemed necessary by company policy, the transaction should not
proceed further until credit is approved.
RETURN POLICY. Because credit approval is generally a credit department function, that depart-
ment authorizes the processing of sales returns as well. An approval determination is based on the na-
ture of the sale and the circumstances of the return. The concepts of specific and general authority
also influence this activity. Most organizations have specific rules for granting cash refunds and cred-
its to customers based on the materiality of the transaction. As materiality increases, credit approval
becomes more formal.
REMITTANCE LIST (CASH PRELIST). The cash prelist provides a means for verifying that cus-
tomer checks and remittance advices match in amount. The presence of an extra remittance advice in the
AR department or the absence of a customer’s check in the cash receipts department would be detected
when the batch is reconciled with the prelist. Thus, the prelist authorizes the posting of a remittance
advice to a customer’s account.