Page 235 - Accounting Information Systems
P. 235
206 PART II Transaction Cycles and Business Processes
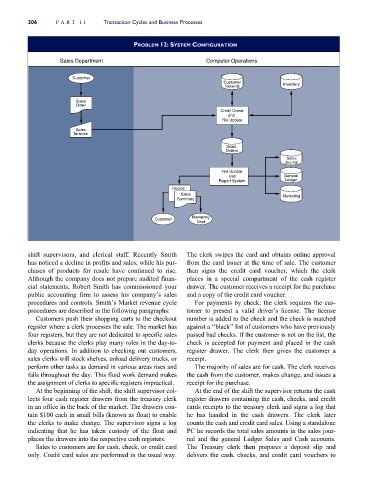
PROBLEM 12: SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
Sales Department Computer Operations
Customer
Customer Inventory
Records
Sales
Order
Credit Check
and
File Update
Sales
Terminal
Sales
Orders
Sales
Journal
File Update
and General
Report System Ledger
Invoice
Sales Marketing
Summary
Marketing
Customer
Dept.
shift supervisors, and clerical staff. Recently Smith The clerk swipes the card and obtains online approval
has noticed a decline in profits and sales, while his pur- from the card issuer at the time of sale. The customer
chases of products for resale have continued to rise. then signs the credit card voucher, which the clerk
Although the company does not prepare audited finan- places in a special compartment of the cash register
cial statements, Robert Smith has commissioned your drawer. The customer receives a receipt for the purchase
public accounting firm to assess his company’s sales and a copy of the credit card voucher.
procedures and controls. Smith’s Market revenue cycle For payments by check, the clerk requires the cus-
procedures are described in the following paragraphs: tomer to present a valid driver’s license. The license
Customers push their shopping carts to the checkout number is added to the check and the check is matched
register where a clerk processes the sale. The market has against a ‘‘black’’ list of customers who have previously
four registers, but they are not dedicated to specific sales passed bad checks. If the customer is not on the list, the
clerks because the clerks play many roles in the day-to- check is accepted for payment and placed in the cash
day operations. In addition to checking out customers, register drawer. The clerk then gives the customer a
sales clerks will stock shelves, unload delivery trucks, or receipt.
perform other tasks as demand in various areas rises and The majority of sales are for cash. The clerk receives
falls throughout the day. This fluid work demand makes the cash from the customer, makes change, and issues a
the assignment of clerks to specific registers impractical. receipt for the purchase.
At the beginning of the shift, the shift supervisor col- At the end of the shift the supervisor returns the cash
lects four cash register drawers from the treasury clerk register drawers containing the cash, checks, and credit
in an office in the back of the market. The drawers con- cards receipts to the treasury clerk and signs a log that
tain $100 each in small bills (known as float) to enable he has handed in the cash drawers. The clerk later
the clerks to make change. The supervisor signs a log counts the cash and credit card sales. Using a standalone
indicating that he has taken custody of the float and PC he records the total sales amounts in the sales jour-
places the drawers into the respective cash registers. nal and the general Ledger Sales and Cash accounts.
Sales to customers are for cash, check, or credit card The Treasury clerk then prepares a deposit slip and
only. Credit card sales are performed in the usual way. delivers the cash, checks, and credit card vouchers to