Page 303 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 303
294 5. PREPROCESSING
scan whole datasets, generally based on a proper in these undesired areas are simply multiplied
amplitude criterion, and then kill the traces that by zero. This process is known as muting and
do not satisfy the criterion. If not applied auto- it can be applied to the seismic data in three dif-
matically, trace kill does not have any parameter ferent implementations:
to be determined. Therefore, the only QC appli-
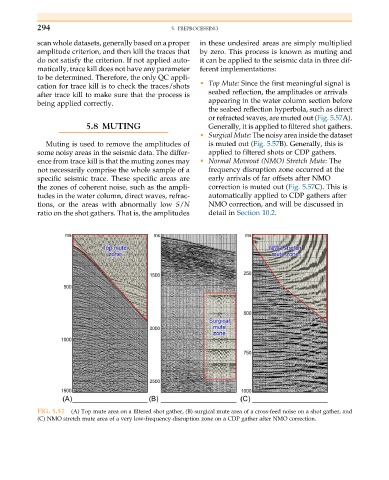
cation for trace kill is to check the traces/shots • Top Mute: Since the first meaningful signal is
seabed reflection, the amplitudes or arrivals
after trace kill to make sure that the process is
appearing in the water column section before
being applied correctly.
the seabed reflection hyperbola, such as direct
or refracted waves, are muted out (Fig. 5.57A).
5.8 MUTING Generally, it is applied to filtered shot gathers.
• Surgical Mute: The noisy area inside the dataset
Muting is used to remove the amplitudes of is muted out (Fig. 5.57B). Generally, this is
some noisy areas in the seismic data. The differ- applied to filtered shots or CDP gathers.
ence from trace kill is that the muting zones may • Normal Moveout (NMO) Stretch Mute: The
not necessarily comprise the whole sample of a frequency disruption zone occurred at the
specific seismic trace. These specific areas are early arrivals of far offsets after NMO
the zones of coherent noise, such as the ampli- correction is muted out (Fig. 5.57C). This is
tudes in the water column, direct waves, refrac- automatically applied to CDP gathers after
tions, or the areas with abnormally low S/N NMO correction, and will be discussed in
ratio on the shot gathers. That is, the amplitudes detail in Section 10.2.
FIG. 5.57 (A) Top mute area on a filtered shot gather, (B) surgical mute area of a cross-feed noise on a shot gather, and
(C) NMO stretch mute area of a very low-frequency disruption zone on a CDP gather after NMO correction.