Page 324 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 324
6. DECONVOLUTION 315
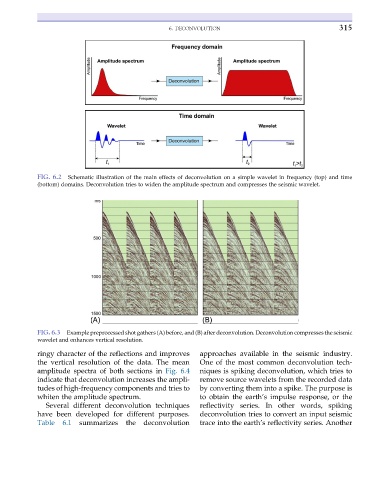
FIG. 6.2 Schematic illustration of the main effects of deconvolution on a simple wavelet in frequency (top) and time
(bottom) domains. Deconvolution tries to widen the amplitude spectrum and compresses the seismic wavelet.
FIG. 6.3 Example preprocessed shot gathers (A) before, and (B) after deconvolution. Deconvolution compresses the seismic
wavelet and enhances vertical resolution.
ringy character of the reflections and improves approaches available in the seismic industry.
the vertical resolution of the data. The mean One of the most common deconvolution tech-
amplitude spectra of both sections in Fig. 6.4 niques is spiking deconvolution, which tries to
indicate that deconvolution increases the ampli- remove source wavelets from the recorded data
tudes of high-frequency components and tries to by converting them into a spike. The purpose is
whiten the amplitude spectrum. to obtain the earth’s impulse response, or the
Several different deconvolution techniques reflectivity series. In other words, spiking
have been developed for different purposes. deconvolution tries to convert an input seismic
Table 6.1 summarizes the deconvolution trace into the earth’s reflectivity series. Another