Page 363 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 363
354 6. DECONVOLUTION
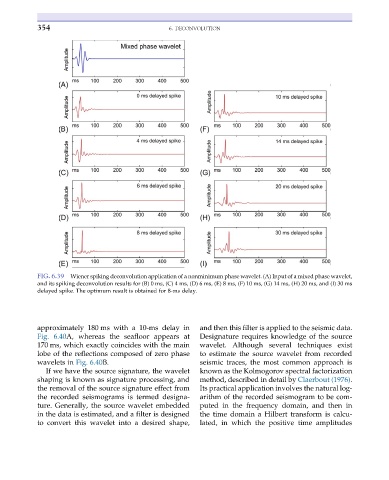
FIG. 6.39 Wiener spiking deconvolution application of a nonminimum phase wavelet. (A) Input of a mixed phase wavelet,
and its spiking deconvolution results for (B) 0 ms, (C) 4 ms, (D) 6 ms, (E) 8 ms, (F) 10 ms, (G) 14 ms, (H) 20 ms, and (I) 30 ms
delayed spike. The optimum result is obtained for 8-ms delay.
approximately 180 ms with a 10-ms delay in and then this filter is applied to the seismic data.
Fig. 6.40A, whereas the seafloor appears at Designature requires knowledge of the source
170 ms, which exactly coincides with the main wavelet. Although several techniques exist
lobe of the reflections composed of zero phase to estimate the source wavelet from recorded
wavelets in Fig. 6.40B. seismic traces, the most common approach is
If we have the source signature, the wavelet known as the Kolmogorov spectral factorization
shaping is known as signature processing, and method, described in detail by Claerbout (1976).
the removal of the source signature effect from Its practical application involves the natural log-
the recorded seismograms is termed designa- arithm of the recorded seismogram to be com-
ture. Generally, the source wavelet embedded puted in the frequency domain, and then in
in the data is estimated, and a filter is designed the time domain a Hilbert transform is calcu-
to convert this wavelet into a desired shape, lated, in which the positive time amplitudes