Page 376 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 376
7. SUPPRESSION OF MULTIPLE REFLECTIONS 367
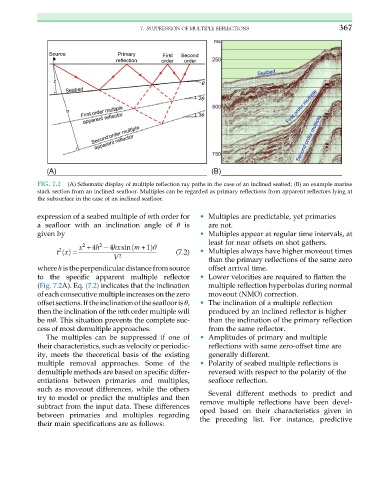
FIG. 7.2 (A) Schematic display of multiple reflection ray paths in the case of an inclined seabed; (B) an example marine
stack section from an inclined seafloor. Multiples can be regarded as primary reflections from apparent reflectors lying at
the subsurface in the case of an inclined seafloor.
expression of a seabed multiple of mth order for • Multiples are predictable, yet primaries
a seafloor with an inclination angle of θ is are not.
given by • Multiples appear at regular time intervals, at
least for near offsets on shot gathers.
2
x +4h 4hxsin m +1Þθ
2
2 ð
t xðÞ ¼ 2 (7.2) • Multiples always have higher moveout times
V
than the primary reflections of the same zero
where h is the perpendicular distance from source offset arrival time.
to the specific apparent multiple reflector • Lower velocities are required to flatten the
(Fig. 7.2A). Eq. (7.2) indicates that the inclination multiple reflection hyperbolas during normal
of each consecutive multiple increases on the zero moveout (NMO) correction.
offsetsections.Iftheinclinationoftheseafloorisθ, • The inclination of a multiple reflection
then the inclination of the mth order multiple will produced by an inclined reflector is higher
be mθ. This situation prevents the complete suc- than the inclination of the primary reflection
cess of most demultiple approaches. from the same reflector.
The multiples can be suppressed if one of • Amplitudes of primary and multiple
their characteristics, such as velocity or periodic- reflections with same zero-offset time are
ity, meets the theoretical basis of the existing generally different.
multiple removal approaches. Some of the • Polarity of seabed multiple reflections is
demultiple methods are based on specific differ- reversed with respect to the polarity of the
entiations between primaries and multiples, seafloor reflection.
such as moveout differences, while the others
Several different methods to predict and
try to model or predict the multiples and then
remove multiple reflections have been devel-
subtract from the input data. These differences
oped based on their characteristics given in
between primaries and multiples regarding
the preceding list. For instance, predictive
their main specifications are as follows: