Page 377 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 377
368 7. SUPPRESSION OF MULTIPLE REFLECTIONS
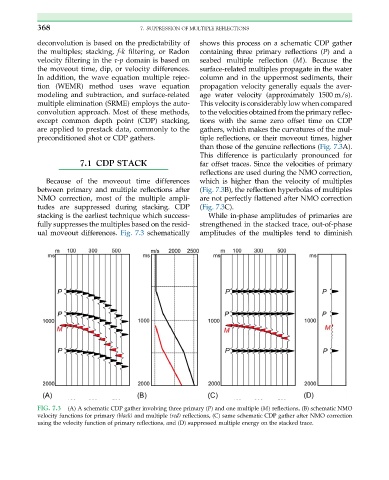
deconvolution is based on the predictability of shows this process on a schematic CDP gather
the multiples; stacking, f-k filtering, or Radon containing three primary reflections (P)and a
velocity filtering in the τ-p domain is based on seabed multiple reflection (M). Because the
the moveout time, dip, or velocity differences. surface-related multiples propagate in the water
In addition, the wave equation multiple rejec- column and in the uppermost sediments, their
tion (WEMR) method uses wave equation propagation velocity generally equals the aver-
modeling and subtraction, and surface-related age water velocity (approximately 1500 m/s).
multiple elimination (SRME) employs the auto- This velocity is considerably low when compared
convolution approach. Most of these methods, to the velocities obtained from the primary reflec-
except common depth point (CDP) stacking, tions with the same zero offset time on CDP
are applied to prestack data, commonly to the gathers, which makes the curvatures of the mul-
preconditioned shot or CDP gathers. tiple reflections, or their moveout times, higher
than those of the genuine reflections (Fig. 7.3A).
This difference is particularly pronounced for
7.1 CDP STACK far offset traces. Since the velocities of primary
reflections are used during the NMO correction,
Because of the moveout time differences which is higher than the velocity of multiples
between primary and multiple reflections after (Fig. 7.3B), the reflection hyperbolas of multiples
NMO correction, most of the multiple ampli- are not perfectly flattened after NMO correction
tudes are suppressed during stacking. CDP (Fig. 7.3C).
stacking is the earliest technique which success- While in-phase amplitudes of primaries are
fully suppresses the multiples based on the resid- strengthened in the stacked trace, out-of-phase
ual moveout differences. Fig. 7.3 schematically amplitudes of the multiples tend to diminish
FIG. 7.3 (A) A schematic CDP gather involving three primary (P) and one multiple (M) reflections, (B) schematic NMO
velocity functions for primary (black) and multiple (red) reflections, (C) same schematic CDP gather after NMO correction
using the velocity function of primary reflections, and (D) suppressed multiple energy on the stacked trace.