Page 375 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 375
366 7. SUPPRESSION OF MULTIPLE REFLECTIONS
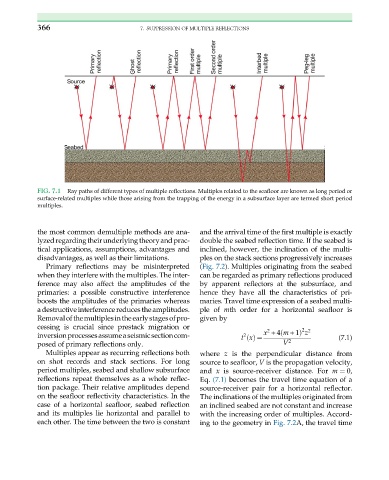
FIG. 7.1 Ray paths of different types of multiple reflections. Multiples related to the seafloor are known as long period or
surface-related multiples while those arising from the trapping of the energy in a subsurface layer are termed short period
multiples.
the most common demultiple methods are ana- and the arrival time of the first multiple is exactly
lyzedregardingtheirunderlyingtheoryandprac- double the seabed reflection time. If the seabed is
tical applications, assumptions, advantages and inclined, however, the inclination of the multi-
disadvantages, as well as their limitations. ples on the stack sections progressively increases
Primary reflections may be misinterpreted (Fig. 7.2). Multiples originating from the seabed
when they interfere with the multiples. The inter- can be regarded as primary reflections produced
ference may also affect the amplitudes of the by apparent reflectors at the subsurface, and
primaries: a possible constructive interference hence they have all the characteristics of pri-
boosts the amplitudes of the primaries whereas maries. Travel time expression of a seabed multi-
adestructiveinterferencereducestheamplitudes. ple of mth order for a horizontal seafloor is
Removalofthemultiplesintheearlystagesofpro- given by
cessing is crucial since prestack migration or 2 2 2
x +4 m +1Þ z
ð
inversionprocessesassumeaseismicsectioncom- 2
t xðÞ ¼ 2 (7.1)
posed of primary reflections only. V
Multiples appear as recurring reflections both where z is the perpendicular distance from
on shot records and stack sections. For long source to seafloor, V is the propagation velocity,
period multiples, seabed and shallow subsurface and x is source-receiver distance. For m ¼ 0,
reflections repeat themselves as a whole reflec- Eq. (7.1) becomes the travel time equation of a
tion package. Their relative amplitudes depend source-receiver pair for a horizontal reflector.
on the seafloor reflectivity characteristics. In the The inclinations of the multiples originated from
case of a horizontal seafloor, seabed reflection an inclined seabed are not constant and increase
and its multiples lie horizontal and parallel to with the increasing order of multiples. Accord-
each other. The time between the two is constant ing to the geometry in Fig. 7.2A, the travel time