Page 378 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 378
7.1 CDP STACK 369
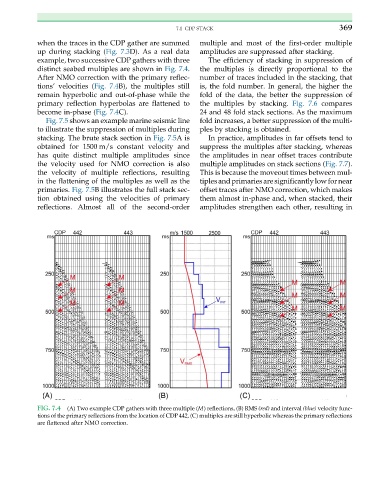
when the traces in the CDP gather are summed multiple and most of the first-order multiple
up during stacking (Fig. 7.3D). As a real data amplitudes are suppressed after stacking.
example, two successive CDP gathers with three The efficiency of stacking in suppression of
distinct seabed multiples are shown in Fig. 7.4. the multiples is directly proportional to the
After NMO correction with the primary reflec- number of traces included in the stacking, that
tions’ velocities (Fig. 7.4B), the multiples still is, the fold number. In general, the higher the
remain hyperbolic and out-of-phase while the fold of the data, the better the suppression of
primary reflection hyperbolas are flattened to the multiples by stacking. Fig. 7.6 compares
become in-phase (Fig. 7.4C). 24 and 48 fold stack sections. As the maximum
Fig. 7.5 shows an example marine seismic line fold increases, a better suppression of the multi-
to illustrate the suppression of multiples during ples by stacking is obtained.
stacking. The brute stack section in Fig. 7.5Ais In practice, amplitudes in far offsets tend to
obtained for 1500 m/s constant velocity and suppress the multiples after stacking, whereas
has quite distinct multiple amplitudes since the amplitudes in near offset traces contribute
the velocity used for NMO correction is also multiple amplitudes on stack sections (Fig. 7.7).
the velocity of multiple reflections, resulting This is because the moveout times between mul-
in the flattening of the multiples as well as the tiplesand primariesare significantly low for near
primaries. Fig. 7.5B illustrates the full stack sec- offset traces after NMO correction, which makes
tion obtained using the velocities of primary them almost in-phase and, when stacked, their
reflections. Almost all of the second-order amplitudes strengthen each other, resulting in
FIG. 7.4 (A) Two example CDP gathers with three multiple (M) reflections, (B) RMS (red) and interval (blue) velocity func-
tions of the primary reflections from the location of CDP 442, (C) multiples are still hyperbolic whereas the primary reflections
are flattened after NMO correction.