Page 402 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 402
7.6 f-k FILTERING 393
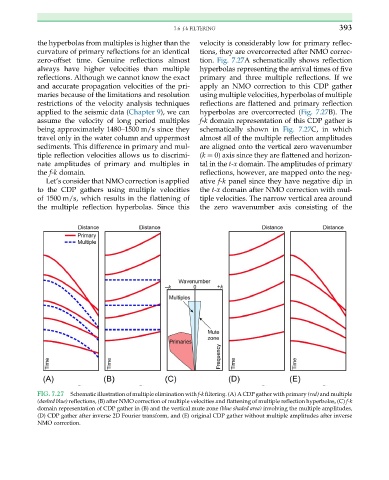
the hyperbolas from multiples is higher than the velocity is considerably low for primary reflec-
curvature of primary reflections for an identical tions, they are overcorrected after NMO correc-
zero-offset time. Genuine reflections almost tion. Fig. 7.27A schematically shows reflection
always have higher velocities than multiple hyperbolas representing the arrival times of five
reflections. Although we cannot know the exact primary and three multiple reflections. If we
and accurate propagation velocities of the pri- apply an NMO correction to this CDP gather
maries because of the limitations and resolution using multiple velocities, hyperbolas of multiple
restrictions of the velocity analysis techniques reflections are flattened and primary reflection
applied to the seismic data (Chapter 9), we can hyperbolas are overcorrected (Fig. 7.27B). The
assume the velocity of long period multiples f-k domain representation of this CDP gather is
being approximately 1480–1500 m/s since they schematically shown in Fig. 7.27C, in which
travel only in the water column and uppermost almost all of the multiple reflection amplitudes
sediments. This difference in primary and mul- are aligned onto the vertical zero wavenumber
tiple reflection velocities allows us to discrimi- (k ¼ 0) axis since they are flattened and horizon-
nate amplitudes of primary and multiples in tal in the t-x domain. The amplitudes of primary
the f-k domain. reflections, however, are mapped onto the neg-
Let’s consider that NMO correction is applied ative f-k panel since they have negative dip in
to the CDP gathers using multiple velocities the t-x domain after NMO correction with mul-
of 1500 m/s, which results in the flattening of tiple velocities. The narrow vertical area around
the multiple reflection hyperbolas. Since this the zero wavenumber axis consisting of the
FIG. 7.27 Schematic illustration of multiple elimination with f-k filtering. (A) A CDP gather with primary (red) and multiple
(dashed blue) reflections, (B) after NMO correction of multiple velocities and flattening of multiple reflection hyperbolas, (C) f-k
domain representation of CDP gather in (B) and the vertical mute zone (blue shaded area) involving the multiple amplitudes,
(D) CDP gather after inverse 2D Fourier transform, and (E) original CDP gather without multiple amplitudes after inverse
NMO correction.