Page 413 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 413
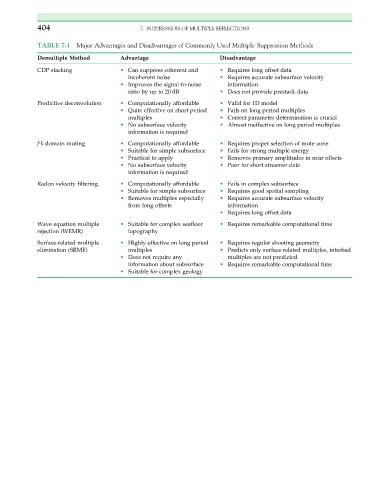
404 7. SUPPRESSION OF MULTIPLE REFLECTIONS
TABLE 7.1 Major Advantages and Disadvantages of Commonly Used Multiple Suppression Methods
Demultiple Method Advantage Disadvantage
CDP stacking • Can suppress coherent and • Requires long offset data
incoherent noise • Requires accurate subsurface velocity
• Improves the signal-to-noise information
ratio by up to 20 dB • Does not provide prestack data
Predictive deconvolution • Computationally affordable • Valid for 1D model
• Quite effective on short period • Fails on long period multiples
multiples • Correct parameter determination is crucial
• No subsurface velocity • Almost ineffective on long period multiples
information is required
f-k domain muting • Computationally affordable • Requires proper selection of mute zone
• Suitable for simple subsurface • Fails for strong multiple energy
• Practical to apply • Removes primary amplitudes in near offsets
• No subsurface velocity • Poor for short streamer data
information is required
Radon velocity filtering • Computationally affordable • Fails in complex subsurface
• Suitable for simple subsurface • Requires good spatial sampling
• Removes multiples especially • Requires accurate subsurface velocity
from long offsets information
• Requires long offset data
Wave equation multiple • Suitable for complex seafloor • Requires remarkable computational time
rejection (WEMR) topography
Surface-related multiple • Highly effective on long period • Requires regular shooting geometry
elimination (SRME) multiples • Predicts only surface related multiples, interbed
• Does not require any multiples are not predicted
information about subsurface • Requires remarkable computational time
• Suitable for complex geology