Page 543 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 543
534 11. SEISMIC MIGRATION
TABLE 11.2 Different Types of Migrations and Their Basic Specifications
Migration Type Specification
Poststack time migration • Valid if stack section equals to zero-offset section
• Adequate in case of diffractions and structural dip
• Handles vertical velocity variations
• Handles smooth lateral velocity variations
• The most computationally efficient migration type
Poststack depth migration • Adequate for excess structural dip
• Handles strong lateral velocity variations
• Less economical than poststack time migration
• Requires an accurate interval velocity-depth model
Prestack time migration • Applied to CDP gathers or common offset sections
(PSTM) • Adequate in case of strong structural complexity
• Solves conflicting dips issue
• Produces image gathers for velocity analysis and AVO
• Less economical than poststack time or depth migrations
Prestack depth migration • Applied to CDP gathers or common offset sections
(PSDM) • Adequate in case of strong structural complexity
• Adequate for excess structural dip
• Handles strong lateral velocity variations
• Less economical than any other migration type
• Requires very accurate interval velocity-depth model
Dip moveout • Simplified version of PSTM
(DMO) • Solves conflicting dips issue
• Followed by a poststack migration
• Velocity analysis is significantly improved
• Assumes a constant velocity model, which induces issues in areas of structural complexity
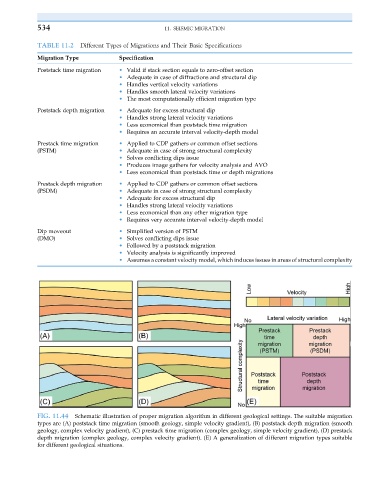
FIG. 11.44 Schematic illustration of proper migration algorithm in different geological settings. The suitable migration
types are (A) poststack time migration (smooth geology, simple velocity gradient), (B) poststack depth migration (smooth
geology, complex velocity gradient), (C) prestack time migration (complex geology, simple velocity gradient), (D) prestack
depth migration (complex geology, complex velocity gradient). (E) A generalization of different migration types suitable
for different geological situations.