Page 539 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 539
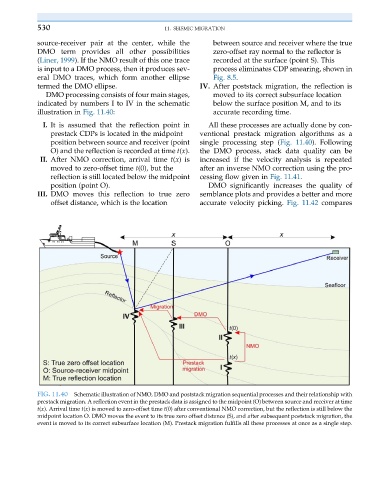
530 11. SEISMIC MIGRATION
source-receiver pair at the center, while the between source and receiver where the true
DMO term provides all other possibilities zero-offset ray normal to the reflector is
(Liner, 1999). If the NMO result of this one trace recorded at the surface (point S). This
is input to a DMO process, then it produces sev- process eliminates CDP smearing, shown in
eral DMO traces, which form another ellipse Fig. 8.5.
termed the DMO ellipse. IV. After poststack migration, the reflection is
DMO processing consists of four main stages, moved to its correct subsurface location
indicated by numbers I to IV in the schematic below the surface position M, and to its
illustration in Fig. 11.40: accurate recording time.
I. It is assumed that the reflection point in All these processes are actually done by con-
prestack CDPs is located in the midpoint ventional prestack migration algorithms as a
position between source and receiver (point single processing step (Fig. 11.40). Following
O) and the reflection is recorded at time t(x). the DMO process, stack data quality can be
II. After NMO correction, arrival time t(x)is increased if the velocity analysis is repeated
moved to zero-offset time t(0), but the after an inverse NMO correction using the pro-
reflection is still located below the midpoint cessing flow given in Fig. 11.41.
position (point O). DMO significantly increases the quality of
III. DMO moves this reflection to true zero semblance plots and provides a better and more
offset distance, which is the location accurate velocity picking. Fig. 11.42 compares
FIG. 11.40 Schematic illustration of NMO, DMO and poststack migration sequential processes and their relationship with
prestack migration. A reflection event in the prestack data is assigned to the midpoint (O) between source and receiver at time
t(x). Arrival time t(x) is moved to zero-offset time t(0) after conventional NMO correction, but the reflection is still below the
midpoint location O. DMO moves the event to its true zero offset distance (S), and after subsequent poststack migration, the
event is moved to its correct subsurface location (M). Prestack migration fulfills all these processes at once as a single step.