Page 100 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 100
GENERAL ADSORPTION PROPERTIES 85
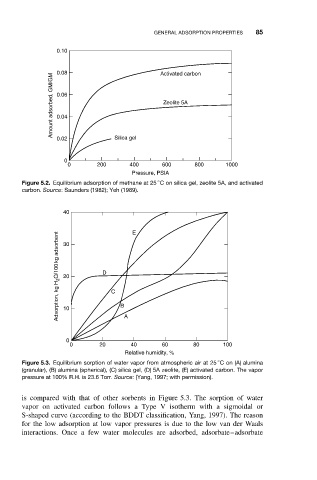
0.10
0.08 Activated carbon
Amount adsorbed, GM/GM 0.06 Zeolite 5A
0.04
0.02 Silica gel
0
0 200 400 600 800 1000
Pressure, PSIA
◦
Figure 5.2. Equilibrium adsorption of methane at 25 C on silica gel, zeolite 5A, and activated
carbon. Source: Saunders (1982); Yeh (1989).
40 E
Adsorption, kg H 2 O/100kg adsorbent 30 D C B
20
10
0 A
0 20 40 60 80 100
Relative humidity, %
◦
Figure 5.3. Equilibrium sorption of water vapor from atmospheric air at 25 Con(A) alumina
(granular), (B) alumina (spherical), (C) silica gel, (D) 5A zeolite, (E) activated carbon. The vapor
pressure at 100% R.H. is 23.6 Torr. Source: (Yang, 1997; with permission).
is compared with that of other sorbents in Figure 5.3. The sorption of water
vapor on activated carbon follows a Type V isotherm with a sigmoidal or
S-shaped curve (according to the BDDT classification, Yang, 1997). The reason
for the low adsorption at low vapor pressures is due to the low van der Waals
interactions. Once a few water molecules are adsorbed, adsorbate–adsorbate