Page 159 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 159
144 SILICA GEL, MCM, AND ACTIVATED ALUMINA
characteristic vibrations of NH 2 and CH 2 groups. The pair of IR bands at 3368
and 3298 cm −1 are due to the asymmetric and symmetric NH 2 stretchings. The
band at 1590 cm −1 is attributed to NH 2 scissoring vibration. The bands at 2931
and 2869 cm −1 are due to CH stretching bands in the group CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 NH 2 .
The amine grafted silicas were stable, as no change was seen in the FTIR spectra
◦
upon heating to 350 C.
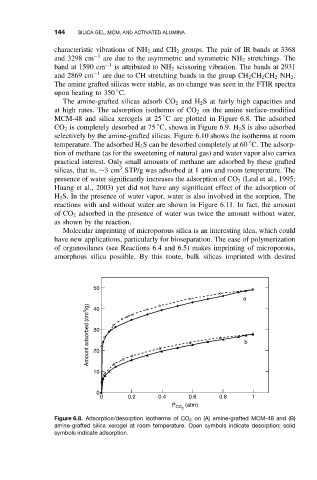
The amine-grafted silicas adsorb CO 2 and H 2 S at fairly high capacities and
at high rates. The adsorption isotherms of CO 2 on the amine surface-modified
◦
MCM-48 and silica xerogels at 25 C are plotted in Figure 6.8. The adsorbed
◦
CO 2 is completely desorbed at 75 C, shown in Figure 6.9. H 2 S is also adsorbed
selectively by the amine-grafted silicas. Figure 6.10 shows the isotherms at room
◦
temperature. The adsorbed H 2 S can be desorbed completely at 60 C. The adsorp-
tion of methane (as for the sweetening of natural gas) and water vapor also carries
practical interest. Only small amounts of methane are adsorbed by these grafted
3
silicas, that is, ∼3cm STP/g was adsorbed at 1 atm and room temperature. The
presence of water significantly increases the adsorption of CO 2 (Leal et al., 1995;
Huang et al., 2003) yet did not have any significant effect of the adsorption of
H 2 S. In the presence of water vapor, water is also involved in the sorption. The
reactions with and without water are shown in Figure 6.11. In fact, the amount
of CO 2 adsorbed in the presence of water was twice the amount without water,
as shown by the reaction.
Molecular imprinting of microporous silica is an interesting idea, which could
have new applications, particularly for bioseparation. The ease of polymerization
of organosilanes (see Reactions 6.4 and 6.5) makes imprinting of microporous,
amorphous silica possible. By this route, bulk silicas imprinted with desired
50
a
Amount adsorbed (cm 3 /g) 30 b
40
20
10
0
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
(atm)
P CO 2
Figure 6.8. Adsorption/desorption isotherms of CO 2 on (A) amine-grafted MCM-48 and (B)
amine-grafted silica xerogel at room temperature. Open symbols indicate desorption; solid
symbols indicate adsorption.