Page 155 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 155
Design procedures 143
6.3 DIFFERENTIAL CONTINUOUS CONTACTING
If the multiple stages described above were to be merged into a continuously
moving bed such as that for solids in plug flow, then a stagewise calculation
procedure could be used to provide the number of equivalent theoretical stages
(or plates) required for the given separation. Given that the height equivalent
to a theoretical plate, HETP, is available for the adsorbate-adsorbent
combination, then the required height of the column would be given by:
L = (number ofequilibrium stages) x HETP (6.14)
Unlike in distillation and absorption, very little is known about HETP
values in adsorption. As a consequence, it may be preferable to use the
transfer unit concept for continuous flow adsorbers like the solids in plug
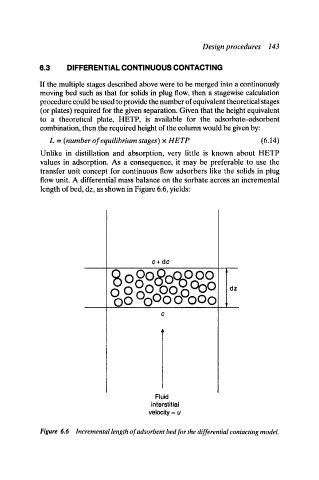
flow unit. A differential mass balance on the sorbate across an incremental
length of bed, dz, as shown in Figure 6.6, yields:
c+dc
..Oo O oo
~
0 C dz
)Y6o Ooo
,oo o"ooo,
oo%
Fluid
interstitial
velocity = u
Figure 6.6 Incremental length of adsorbent bed for the differential contacting model