Page 23 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 23
20 Adsorbents
prevent oxidation of the carbon. Being a combustion process, tight controls
on environmental discharges are in place and the regeneration process is
prescribed for Integrated Pollution Control by the UK's Environment
Agency.
In powdered form activated carbon can be used directly, usually in batch
applications, but it cannot then be recovered easily for regeneration. Two
possibilities exist. First powdered activated carbon can be filtered off in
batch processing for subsequent regeneration. Alternatively, it can remain
in the sludge in water treament applications for subsequent disposal.
2.2 CARBON MOLECULAR SIEVES (CMS)
Special manufacturing procedures can be used to make amorphous carbons
which have a very narrow distribution of pore sizes with effective diameters
ranging from 0.4-0.9 nm. Raw materials can be chemicals such as poly-
vinylidene dichloride and phenolic resin, or naturally occurring materials
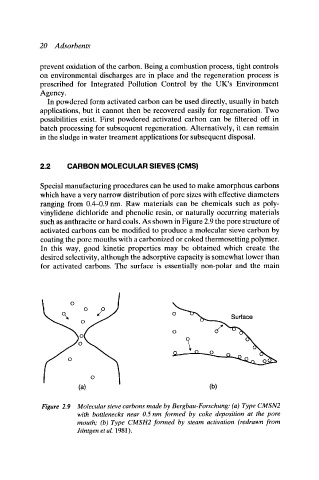
such as anthracite or hard coals. As shown in Figure 2.9 the pore structure of
activated carbons can be modified to produce a molecular sieve carbon by
coating the pore mouths with a carbonized or coked thermosetting polymer.
In this way, good kinetic properties may be obtained which create the
desired selectivity, although the adsorptive capacity is somewhat lower than
for activated carbons. The surface is essentially non-polar and the main
~
Surface
o o
o
(a) (b)
Figure 2.9 Molecular sieve carbons made by Bergbau-Forschung: (a) Type CMSN2
with bottlenecks near 0.5 nm formed by coke deposition at the pore
mouth; (b) Type CMSH2 formed by steam activation (redrawn from
JEintgen et al. 1981).