Page 57 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 57
54 Fundamentals of adsorption equilibria
1.2
Y
v
1.o r~ Y
V
V
0.8
o
o
.6 '-
n V
0.4 -
V YA
O.2 -
....... I I I I I t I , I I "~
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
q21q~ Less volatile
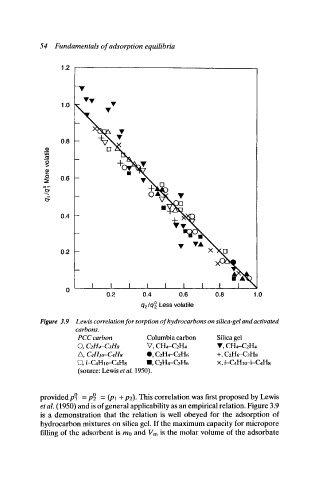
Figure 3.9 Lewis correlation for sorption of hydrocarbons on silica-gel and activated
carbons.
PCC carbon Columbia carbon Silica gel
V, CH4-C2H4
(3, C2H4--C3Hs V, CH4-C2H4
/k, C4HIo-C4H8 O, C2H4-C2H6 +, C2H6-C3H8
ISl, i-C4Hlo--C4H8 II, CEH4-CaH6 • i-C4H 10-i-C4H8
(source: Lewis et al. 1950).
provided pO = pO _ (pl + p2). This correlation was first proposed by Lewis
et al. (1950) and is of general applicability as an empirical relation. Figure 3.9
is a demonstration that the relation is well obeyed for the adsorption of
hydrocarbon mixtures on silica gel. If the maximum capacity for micropore
filling of the adsorbent is mo and Vm is the molar volume of the adsorbate