Page 59 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 59
56 Fundamentals of adsorption equilibria
total adsorbed volume of the mixture. From data for pure component
adsorption, the mole fraction xi of component i in the mixture can be
computed. This is accomplished by an iterative procedure, first assuming an
xi and calculating (e/V'm)i from equation (3.37) adopting values of
fi and fsi from single component data. The correct values for the set xi
correspond to (e/V'm)i being the same for all components. Thus the
molar volume of the mixture may be found because it is assumed that
molar volumes are additive such that (Vmix) for the mixture is ~xiVmi and
ni - xi nT. The molar volume, Vmi, is that of the saturated liquid at the
temperature which corresponds to the saturated vapour pressure psi (= yi
P/xi) where yi is the mole fraction of i in the vapour phase and P the total
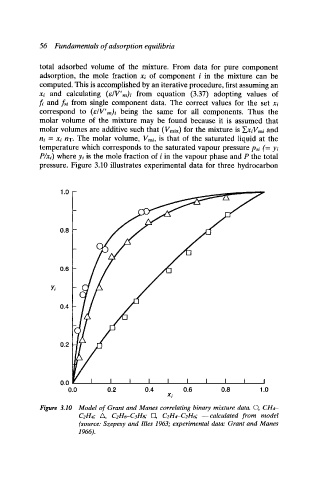
pressure. Figure 3.10 illustrates experimental data for three hydrocarbon
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
I I I I I I I I
,,I . I
0.0 i
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
xi
Figure 3.10 Model of Grant and Manes correlating binary mixture data. O, CH4-
C2H4," A, C2HD-C3Hs; [=], C2H4-C2H6; m calculaled from model
(source: Szepesy and llles 1963; experimental data: Grant and Manes
1966).