Page 65 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 65
62 Fundamentals of adsorption equilibria
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
00[g I I I I
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
xi
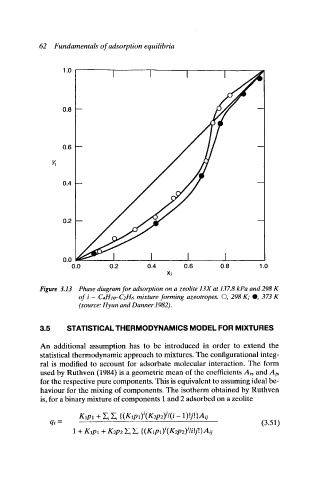
Figure 3.13 Phase diagram for adsorption on a zeolite 13X at 13Z8 kPa and 298 K
of i - C4H1o-C2H6 mixture forming azeotropes. y 298 K; @, 373 K
(source: Hyun and Danner 1982).
3.5 STATISTICAL THERMODYNAMICS MODEL FOR MIXTURES
An additional assumption has to be introduced in order to extend the
statistical thermodynamic approach to mixtures. The configurational integ-
ral is modified to account for adsorbate molecular interaction. The form
used by Ruthven (1984) is a geometric mean of the coefficients Ais and Ajs
for the respective pure components. This is equivalent to assuming ideal be-
haviour for the mixing of components. The isotherm obtained by Ruthven
is, for a binary mixture of components I and 2 adsorbed on a zeolite
Klpl + ~j ~,, {(K~pl)i(KEpE)J/(i - 1)!j!}Aiy
qi = (3.51)
1 + Klpl + K2p2 ~j ~,, {(K~pl)i(KEp2)J/i!j!}Aiy