Page 10 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 10
Else_AIEC-INGLE_Ch001.qxd 7/13/2006 1:53 PM Page 6
6 1. Air and ater Pollution W
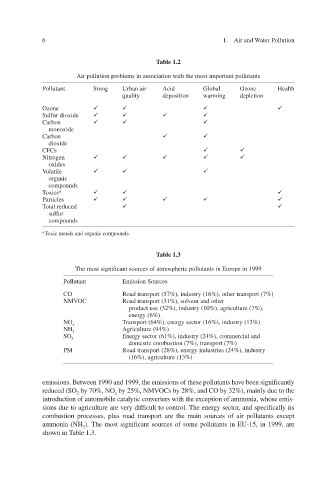
Table 1.2
Air pollution problems in association with the most important pollutants
Pollutant Smog Urban air Acid Global Ozone Health
quality deposition warming depletion
Ozone
Sulfur dioxide
Carbon
monoxide
Carbon
dioxide
CFCs
Nitrogen
oxides
Volatile
organic
compounds
Toxics a
Particles
Total reduced
sulfur
compounds
a Toxic metals and organic compounds.
Table 1.3
The most significant sources of atmospheric pollutants in Europe in 1999
Pollutant Emission Sources
CO Road transport (57%), industry (16%), other transport (7%)
NMVOC Road transport (31%), solvent and other
product use (32%), industry (10%), agriculture (7%),
energy (6%)
NO x Transport (64%), energy sector (16%), industry (13%)
NH 3 Agriculture (94%)
SO 2 Energy sector (61%), industry (24%), commercial and
domestic combustion (7%), transport (7%)
PM Road transport (28%), energy industries (24%), industry
(16%), agriculture (13%)
emissions. Between 1990 and 1999, the emissions of these pollutants have been significantly
reduced (SO 2 by 70%, NO x by 25%, NMVmainly due to the OCs by 28%, and CO by 32%),
introduction of automobile catalytic converters with the exception of ammonia, whose emis-
f ery dif sions due to agriculture are vicult to control. The energy sector, and specif ically its
combustion processes, plus road transport are the main sources of air pollutants e xcept
ammonia (NH 3 ). The most significant sources of some pollutants in EU-15, in 1999, are
shown in Table 1.3.