Page 102 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 102
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH003.qxd 7/13/2006 1:45 PM Page 98
98 3. Heterogeneous Processes and Reactor Analysis
100
50
10
P
N
1
5
2 3
4
5
2
6
1
1 10 100 1000 10000
N Re
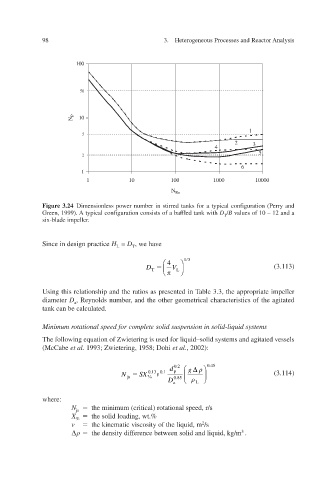
Figure 3.24 Dimensionless power number in stirred tanks for a typical configuration (Perry and
Green, 1999). A typical configuration consists of a baffled tank with D T / B values of 10 – 12 and a
six-blade impeller.
Since in design practice H L = D T , we ha e v
4 13
D V L (3.113)
T
Using this relationship and the ratios as presented in Table 3.3, the appropriate impeller
diameter D a , Reynolds number and the other geometrical characteristics of the agitated
,
tank can be calculated.
Minimum rotational speed for complete solid suspension in solid-liquid systems
The following equation of Zwietering is used for liquid–solid systems and agitated vessels
(McCabe et al . 1993; Zwietering, 1958; Dohi et al ., 2002):
0.2 0.45
d p g
N S 0.13 0.1 (3.114)
X
js % 0.85
D a L
where:
N the minimum (critical) rotational speed, r/s
js
X the solid loading, wt.%
%
v the kinematic viscosity of the liquid, m 2 /s
the density difference between solid and liquid, kg/m 3 .