Page 100 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 100
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH003.qxd 7/13/2006 1:45 PM Page 96
96 3. Heterogeneous Processes and Reactor Analysis
Table 3.3
Geometrical ratios (Perry and Green, 1999; T 1980; McCabe ybal, re et al ., 1993; Nouri and
R.M.Hockey, 1998; Armenante and Nagamine, 1998; P a vlo v et al ., 1979; Fishwick et al ., 2003;
Kato et al ., 2001; Re w atkar et al ., 1991)
Ratio Description Range
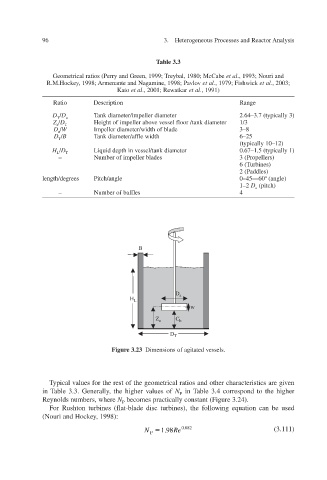
D T / D a Tank diameter/impeller diameter 2.64–3.7 (typically 3)
Z / D T Height of impeller aboessel floor /tank diameter e v v 1/3
a
D a / W Impeller diameter/width of blade 3–8
D T / B Tank diameter/affle width 6–25
(typically 10–12)
H L / D T Liquid depth in vessel/tank diameter 0.67–1.5 (typically 1)
– Number of impeller blades 3 (Propellers)
6 (Turbines)
2 (P addles)
length/degrees Pitch/angle 0–45—60° (angle)
1–2 D a (pitch)
– Number of baf fles 4
B
D a
H L
w
Z a C b
D T
Figure 3.23 Dimensions of agitated v essels.
Typical values for the rest of the geometrical ratios and other characteristics are gi en v
in Table 3.3. Generally the higher values of N P in Table 3.4 correspond to the higher
,
Reynolds numbers, where N P becomes practically constant (Figure 3.24).
For Rushton turbines (flat-blade disc turbines), the following equation can be used
y e (Nouri and Hock, 1998):
N 1.98 Re 0.082 (3.111)
P