Page 194 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 194
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH003.qxd 7/13/2006 1:46 PM Page 190
190 3. Heterogeneous Processes and Reactor Analysis
However, there are also some drawbacks associated with the use of fluidized beds. The
complete mixing of the gas phase in this type of reactor decreases the process dri ving
v force. Moreoer, the formation of large bes the process less ef icient and dif i- ubbles mak f f
we
,
v
cult to handle. Ho the main disadvantages of fluidized beds are the erosion of the
er
reactor, the attrition of the solids, and the irregular conduction between the gas and the
solid phase (McCabe et al ., 1983).
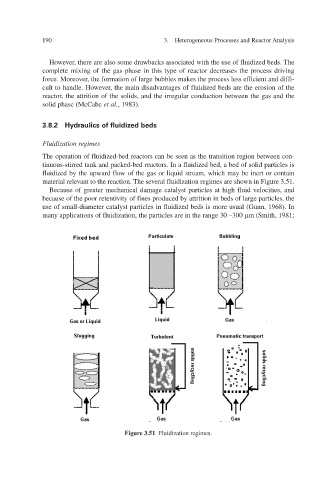
3.8.2 Hydraulics of fluidized beds
Fluidization regimes
The operation of fluidized-bed reactors can be seen as the transition region between con-
tinuous-stirred tank and packed-bed reactors. In a fluidized bed, a bed of solid particles is
fluidized by the upward flow of the gas or liquid stream, which may be inert or contain
material relevant to the reaction. The several fluidization regimes are shown in Figure 3.51.
Because of greater mechanical damage catalyst particles at high fluid v and elocities,
vity of f because of the poor retentiines produced by attrition in beds of lar the ge particles,
use of small-diameter catalyst particles in fluidized beds is more usual (Gunn, 1968). In
many applications of fluidization, the particles are in the range 30 –300 µm (Smith, 1981;
Figure 3.51 Fluidization re gimes.