Page 324 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 324
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH004.qxd 7/1/2006 6:53 PM Page 320
320 4. Adsorption and Ion Exchange
1
0.8
0.6
X
0.4
0.2 ζ =0.0001
ζ =1
ζ =10000
0
-5 -3 -1 1 3 5
Θτ -X τ
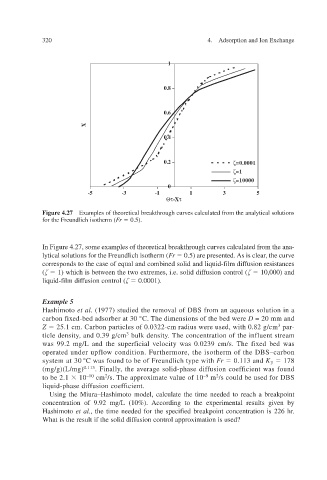
Figure 4.27 Examples of theoretical breakthrough curves calculated from the analytical solutions
for the Freundlich isotherm ( Fr 0.5).
In Figure 4.27, some e es calculated from the ana- xamples of theoretical breakthrough curv
lytical solutions for the Freundlich isotherm ( Fr 0.5) are presented. the curv , As is clear e
corresponds to the case of equal and combined solid and liquid-film diffusion resistances
( 1) which is between the two e i.e. solid diffusion control ( xtremes, 10,000) and
liquid-film diffusion control ( 0.0001).
Example 5
Hashimoto et al . (1977) studied the removal of DBS from an aqueous solution in a
carbon fixed-bed adsorber at 30 °C. The dimensions of the bed were D = 20 mm and
Z 25.1 cm. Carbon particles of 0.0322-cm radius were used, with 0.82 g/cm 3 par-
ticle density and 0.39 g/cm 3 bulk densityThe concentration of the influent stream
.
,
was 99.2 mg/L and the superficial velocity was 0.0239 cm/s. The fixed bed was
operated under upflow condition. Furthermore, the isotherm of the DBS–carbon
system at 30 °C was found to be of Fr eundlich type with Fr 0.113 and K 178
F
(mg/g)(L/mg) 0.113 . Finally the average solid-phase diffusion coefficient was found
,
to be 2.1 10 –10 cm 2 /s. The approximate value of 10 –9 m 2 /s could be used for DBS
liquid-phase diffusion coefficient.
Using the Miura–Hashimoto model, calculate the time needed to reach a breakpoint
concentration of 9.92 mg/L (10%). According to the experimental results gien by v
Hashimoto et al ., the time needed for the specified breakpoint concentration is 226 hr .
What is the result if the solid diffusion control approximation is used?