Page 242 - Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of Structures
P. 242
Example of a Steel Frame Building With Masonry Infill Walls Chapter 4 235
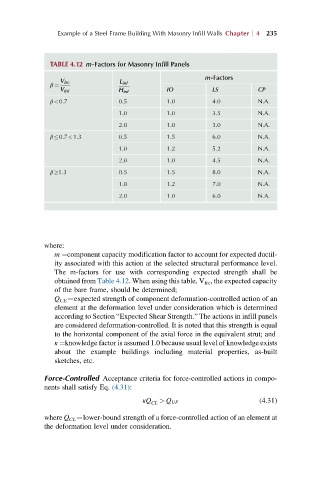
TABLE 4.12 m-Factors for Masonry Infill Panels
m-Factors
V fre L inf
β ¼
V inf H inf IO LS CP
β<0.7 0.5 1.0 4.0 N.A.
1.0 1.0 3.5 N.A.
2.0 1.0 3.0 N.A.
β 0.7<1.3 0.5 1.5 6.0 N.A.
1.0 1.2 5.2 N.A.
2.0 1.0 4.5 N.A.
β 1.3 0.5 1.5 8.0 N.A.
1.0 1.2 7.0 N.A.
2.0 1.0 6.0 N.A.
where:
m ¼component capacity modification factor to account for expected ductil-
ity associated with this action at the selected structural performance level.
The m-factors for use with corresponding expected strength shall be
obtained from Table 4.12. When using this table, V fre , the expected capacity
of the bare frame, should be determined;
Q CE ¼expected strength of component deformation-controlled action of an
element at the deformation level under consideration which is determined
according to Section “Expected Shear Strength.” The actions in infill panels
are considered deformation-controlled. It is noted that this strength is equal
to the horizontal component of the axial force in the equivalent strut; and
κ ¼knowledge factor is assumed 1.0 because usual level of knowledge exists
about the example buildings including material properties, as-built
sketches, etc.
Force-Controlled Acceptance criteria for force-controlled actions in compo-
nents shall satisfy Eq. (4.31):
κQ CL > Q UF (4.31)
where Q CL ¼lower-bound strength of a force-controlled action of an element at
the deformation level under consideration.