Page 53 - Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of Structures
P. 53
Example of a Two-Story Unreinforced Masonry Building Chapter 2 45
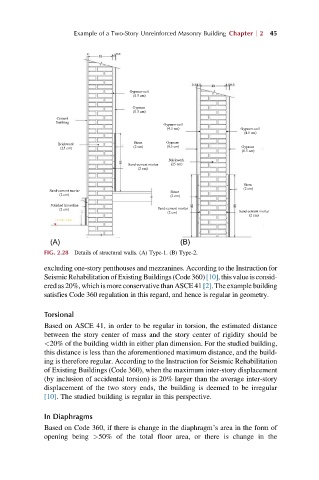
Gypsum-soil
(4.5 cm)
Gypsum
(0.5 cm)
Cement
finishing
Gypsum-soil
(4.5 cm) Gypsum-soil
(4.5 cm)
Stone Gypsum
Brickwork
(25 cm) (2 cm) (0.5 cm) Gypsum
(0.5 cm)
Brickwork
Sand-cement mortar (25 cm)
(2 cm)
Stone
(2 cm)
Sand-cement mortar Stone
(2 cm) (2 cm)
Polished travertine
(2 cm) Sand-cement mortar Sand-cement mortar
(2 cm)
(2 cm)
(A) (B)
FIG. 2.28 Details of structural walls. (A) Type-1. (B) Type-2.
excluding one-story penthouses and mezzanines. According to the Instruction for
Seismic Rehabilitation of Existing Buildings (Code 360) [10], this value is consid-
ered as 20%, which is more conservative than ASCE 41 [2]. The example building
satisfies Code 360 regulation in this regard, and hence is regular in geometry.
Torsional
Based on ASCE 41, in order to be regular in torsion, the estimated distance
between the story center of mass and the story center of rigidity should be
<20% of the building width in either plan dimension. For the studied building,
this distance is less than the aforementioned maximum distance, and the build-
ing is therefore regular. According to the Instruction for Seismic Rehabilitation
of Existing Buildings (Code 360), when the maximum inter-story displacement
(by inclusion of accidental torsion) is 20% larger than the average inter-story
displacement of the two story ends, the building is deemed to be irregular
[10]. The studied building is regular in this perspective.
In Diaphragms
Based on Code 360, if there is change in the diaphragm’s area in the form of
opening being >50% of the total floor area, or there is change in the