Page 101 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 101
80 the analysis, the conclusion reached is that delocalization (hyperconjugation) is the
principal factor favoring the staggered conformation. 107
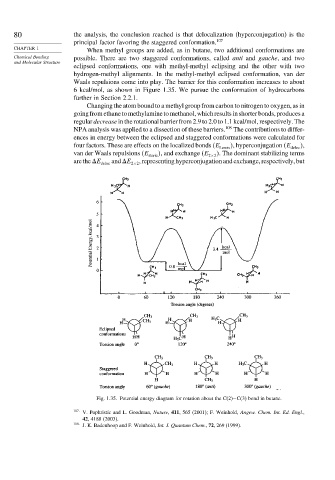
CHAPTER 1 When methyl groups are added, as in butane, two additional conformations are
Chemical Bonding possible. There are two staggered conformations, called anti and gauche, and two
and Molecular Structure
eclipsed conformations, one with methyl-methyl eclipsing and the other with two
hydrogen-methyl alignments. In the methyl-methyl eclipsed conformation, van der
Waals repulsions come into play. The barrier for this conformation increases to about
6 kcal/mol, as shown in Figure 1.35. We pursue the conformation of hydrocarbons
further in Section 2.2.1.
Changing the atom bound to a methyl group from carbon to nitrogen to oxygen, as in
goingfromethanetomethylaminetomethanol,whichresultsinshorterbonds,producesa
regular decrease in the rotational barrier from 2.9 to 2.0 to 1.1 kcal/mol, respectively. The
NPA analysis was applied to a dissection of these barriers. 108 The contributions to differ-
ences in energy between the eclipsed and staggered conformations were calculated for
four factors. These are effects on the localized bonds E Lewis , hyperconjugation E deloc ,
van der Waals repulsions E steric , and exchange E 2×2 . The dominant stabilizing terms
are the
E deloc and
E 2×2 , representing hyperconjugation and exchange, respectively, but
Fig. 1.35. Potential energy diagram for rotation about the C(2)−C(3) bond in butane.
107
V. Pophristic and L. Goodman, Nature, 411, 565 (2001); F. Weinhold, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.,
42, 4188 (2003).
108 J. K. Badenhoop and F. Weinhold, Int. J. Quantum Chem., 72, 269 (1999).