Page 1048 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1048
1032 centered mainly on carbon, but also on the oxygen. 166 Acyl radicals are nucleophilic,
based on their reactivity toward protonated heterocyclic molecules. 167 The acyl radical
CHAPTER 11
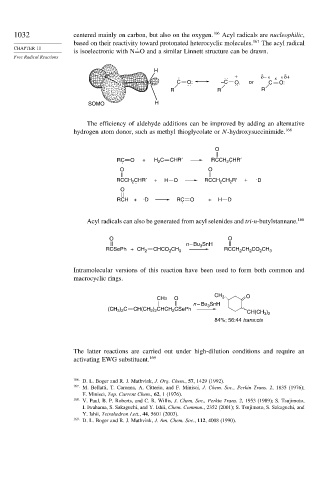
is isoelectronic with N=O and a similar Linnett structure can be drawn.
Free Radical Reactions
H
. : + δ− ο x ο δ+
O C –C or C O:
G O: : O. :
R R R
SOMO H
The efficiency of aldehyde additions can be improved by adding an alternative
hydrogen atom donor, such as methyl thioglycolate or N-hydroxysuccinimide. 168
O
RC . O + H 2 C CHR′ RCCH 2 CHR′
.
O O
RCCH CHR′ + H D RCCH 2 CH R′ + . D
2 .
2
O
RCH + . D RC . O + H D
Acyl radicals can also be generated from acyl selenides and tri-n-butylstannane. 166
O O
n – Bu SnH
3
RCSePh + CH 2 CHCO CH 3 RCCH CH CO CH 3
2
2
2
2
Intramolecular versions of this reaction have been used to form both common and
macrocyclic rings.
CH 3 O
CH3 O
n – Bu SnH
3
(CH ) C CH(CH ) CHCH CSePh
3 2
2
2 2
)
CH(CH 3 2
84%; 56:44 trans:cis
The latter reactions are carried out under high-dilution conditions and require an
activating EWG substituent. 169
166
D. L. Boger and R. J. Mathvink, J. Org. Chem., 57, 1429 (1992).
167 M. Bellatti, T. Caronna, A. Citterio, and F. Minisci, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1835 (1976);
F. Minisci, Top. Current Chem., 62, 1 (1976).
168 V. Paul, B. P. Roberts, and C. R. Willis, J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 2, 1953 (1989); S. Tsujimoto,
I. Iwahama, S. Sakaguchi, and Y. Ishii, Chem. Commun., 2352 (2001); S. Tsujimoto, S. Sakaguchi, and
Y. Ishii, Tetrahedron Lett., 44, 5601 (2003).
169
D. L. Boger and R. J. Mathvink, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112, 4008 (1990).