Page 668 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 668
650
250 231.4
(14)
CHAPTER 7
200
Addition, Condensation
and Substitution 139.0
Reactions of Carbonyl 150 (17) 143.7 (23)
Compounds
112.3 (2)
88.0
100 (26)
111.9
(20)
50 37.6 (5) 67.9
(29)
10.2 (15) 9.5 (30)
8.8 5.0
0 10.9 5.5 14.7 (21) (27)
0.0 (8) (10) 0.0 0.0 1.7 (24)
(1,4,7) (9) –46.0 (3) (13,16,19) 1.5 (18) (22,25,28)
–50.9
–50 (6)
–57.6 (11)
(a) (b) (c)
80.9
63.8
97.1
1.252 1.505
123.8
1.346 1.825 94.5 1.171
75.0 1.348 91.5 1.452
1.563 110.3
1.466
1.422 1.343
78.2 73.9
74.1 112.9 14 23
1.196
2
88.4 108.5
101.7 1.499
1.344 1.985 1.155 1.174
161.6 163.8
103.6
108.3 1.225 1.308 1.307 105.6 1.257
1.552 156.7 105.7 87.5 1.423 98.9
102.7
1.230
98.3 0.989
82.2
1.177 2.155
148.9 1.370
122.9
1.133 1.451 17 26
148.9
5
89.5
108.8
105.8 165.2
1.074
168.8 1.275
1.347
1.133 1.430 1.495 179.0
1.319 2.085 1.158
112.6 110.2 110.9
110.1
98.3
1.544 1.288 1.411 112.5
1.311 1.298 168.5 1.014
106.9 167.5 115.3
95.2 1.156 112.4 177.8
1.014
96.8 1.138 1.104 1.487 1.624
1.112
1.484
170.5 164.1 0.973
10 20 29
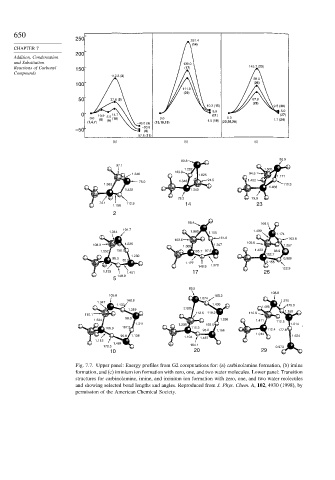
Fig. 7.7. Upper panel: Energy profiles from G2 computations for: (a) carbinolamine formation, (b) imine
formation, and (c) iminium ion formation with zero, one, and two water molecules. Lower panel: Transition
structures for carbinolamine, imine, and iminium ion formation with zero, one, and two water molecules
and showing selected bond lengths and angles. Reproduced from J. Phys. Chem. A, 102, 4930 (1998), by
permission of the American Chemical Society.