Page 11 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 11
xii
O O
Introduction Y OH Directed
+ R R 1 Xrearrangement
R X 2 (10.1) R X + Ar-H
Alkenyl-silane or R O Aromatic
stannane acylation (9.2, 9.3) O R
acylation (11.1)
R R Ar
R O O –
O
2 R + C O O 1 R R R R + R-X
R
2 R Enolate alkylation (1.2)
hydroboration- R
carbonylation (9.1) R R R
O O –
R R EWG
SnBu + R R +
3 O R
Ar X + C O EWG
Palladium-catalyzed R Ar ketone Conjugate Addition (2.6)
carbonylation (8.2) structure
O OH O –
O
O R + O CHR
R
+ R M R R or R
R X O
Aldol addition or
O condensation (2.1)
Organometalic R R
addition (7.2) R
R O O
R R
R R
R O
EWG + R
O [3,3]-sigmatropic
rearrangement (6.4) R X
R EWG
R
Enolate acylation (2.3)
R
Alkene hydroboration/oxidation (4.5)
or Pd-catalyzed oxidation (8.2)
X = halide or sulfonate leaving group EWG = Electron-releasing group
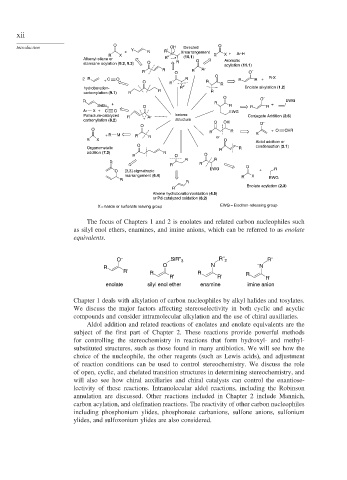
The focus of Chapters 1 and 2 is enolates and related carbon nucleophiles such
as silyl enol ethers, enamines, and imine anions, which can be referred to as enolate
equivalents.
O – SiR" 3 R" 2 R"
O N –
R N
R' R R
R' R' R R'
enolate silyl enol ether enamine imine anion
Chapter 1 deals with alkylation of carbon nucleophiles by alkyl halides and tosylates.
We discuss the major factors affecting stereoselectivity in both cyclic and acyclic
compounds and consider intramolecular alkylation and the use of chiral auxiliaries.
Aldol addition and related reactions of enolates and enolate equivalents are the
subject of the first part of Chapter 2. These reactions provide powerful methods
for controlling the stereochemistry in reactions that form hydroxyl- and methyl-
substituted structures, such as those found in many antibiotics. We will see how the
choice of the nucleophile, the other reagents (such as Lewis acids), and adjustment
of reaction conditions can be used to control stereochemistry. We discuss the role
of open, cyclic, and chelated transition structures in determining stereochemistry, and
will also see how chiral auxiliaries and chiral catalysts can control the enantiose-
lectivity of these reactions. Intramolecular aldol reactions, including the Robinson
annulation are discussed. Other reactions included in Chapter 2 include Mannich,
carbon acylation, and olefination reactions. The reactivity of other carbon nucleophiles
including phosphonium ylides, phosphonate carbanions, sulfone anions, sulfonium
ylides, and sulfoxonium ylides are also considered.