Page 740 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 740
716 R
Pd 0
R X + CH CH Z R CH CH Z or CH 2 C Z
CHAPTER 8 2
Reactions Involving
Transition Metals R = alkenyl, aryl
X = halide, sulfonate
Many procedures use Pd OAc or other Pd(II) salts as catalysts with the catalytic-
2
ally active Pd(0) being generated in situ. The reactions are usually carried out in the
presence of a phosphine ligand, with tris-o-tolylphosphine being preferred in many
cases. Tris-(2-furyl)phosphine (tfp) is also used frequently. Several chelating diphos-
phines, shown below with their common abbreviations, are also effective. Phosphites
are also good ligands. 130
Ph 2 PCH 2 CH 2 PPh 2
dppe PPh 2
Fe PAr 2
PAr 2
PPh 2
Ph P(CH ) PPh 2
2
2 3
dppp dppf
CH 3 CH
3
DINAP Ar = phenyl
Ph 2 P(CH ) PPh 2 Ph P PPh 2 tol–DINAP Ar = o -tolyl
2 4
2
dppb
chiraphos
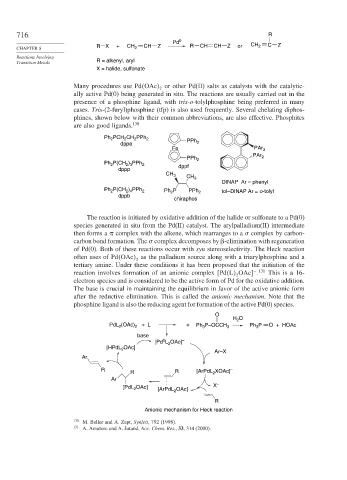
The reaction is initiated by oxidative addition of the halide or sulfonate to a Pd(0)
species generated in situ from the Pd(II) catalyst. The arylpalladium(II) intermediate
then forms a complex with the alkene, which rearranges to a complex by carbon-
carbon bond formation. The complex decomposes by -elimination with regeneration
of Pd(0). Both of these reactions occur with syn stereoselectivity. The Heck reaction
often uses of Pd OAc as the palladium source along with a triarylphosphine and a
2
tertiary amine. Under these conditions it has been proposed that the initiation of the
− 131
reaction involves formation of an anionic complex Pd L OAc
. This is a 16-
2
electron species and is considered to be the active form of Pd for the oxidative addition.
The base is crucial in maintaining the equilibrium in favor of the active anionic form
after the reductive elimination. This is called the anionic mechanism. Note that the
phosphine ligand is also the reducing agent for formation of the active Pd(0) species.
O
H O
2
PdL (OAc) + L + Ph 3 P–OCCH 3 Ph P O + HOAc
2
2
3
base
0
[Pd L OAc] –
2
[HPdL OAc]
2
Ar–X
Ar
R R [ArPdL XOAc] –
R 2
Ar
OAc] X –
[PdL 2 [ArPdL OAc]
2
R
Anionic mechanism for Heck reaction
130 M. Beller and A. Zapt, Synlett, 792 (1998).
131
A. Amatore and A. Jutand, Acc. Chem. Res., 33, 314 (2000).