Page 932 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 932
908 There is a small dependence on the rate of solvent insertion reactions for saturated
hydrocarbons. 121 Benzene is much less reactive.
CHAPTER 10
Reactions Involving
2 3
2 4
3
3 2
Carbocations, Carbenes, (CH ) CH(CH ) CH 3 CH (CH ) CH 3
and Radicals as Reactive
Intermediates
4 –1
4 –1
4 –1
7.1 x 10 s 1.9 x 10 s 2.8 x 10 s
Absolute rate for solvent insertion by 4-methylphenylchlorocarbene
∗
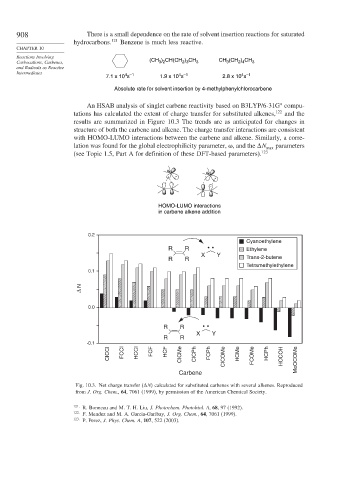
An HSAB analysis of singlet carbene reactivity based on B3LYP/6-31G compu-
tations has calculated the extent of charge transfer for substituted alkenes, 122 and the
results are summarized in Figure 10.3 The trends are as anticipated for changes in
structure of both the carbene and alkene. The charge transfer interactions are consistent
with HOMO-LUMO interactions between the carbene and alkene. Similarly, a corre-
lation was found for the global electrophilicity parameter, , and the
N max parameters
(see Topic 1.5, Part A for definition of these DFT-based parameters). 123
:
:
HOMO-LUMO interactions
in carbene alkene addition
0.2
Cyanoethylene
R R Ethylene
X Y
R R Trans-2-butene
Tetramethyiethylene
0.1
Δ N
0.0
R R
X Y
R R
-0.1
CICCI FCCI HCCI FCF HCF CICMe CICPh FCPh CICOMe HCMe FCOMe HCPh HOCOH MeOCOMe
Carbene
Fig. 10.3. Net charge transfer (
N calculated for substituted carbenes with several alkenes. Reproduced
from J. Org. Chem., 64, 7061 (1999), by permission of the American Chemical Society.
121
R. Bonneau and M. T. H. Liu, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 68, 97 (1992).
122 F. Mendez and M. A. Garcia-Garibay, J. Org. Chem., 64, 7061 (1999).
123
P. Perez, J. Phys. Chem. A, 107, 522 (2003).