Page 304 - Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers, Second Edition
P. 304
12.13 PROBLEMS 293
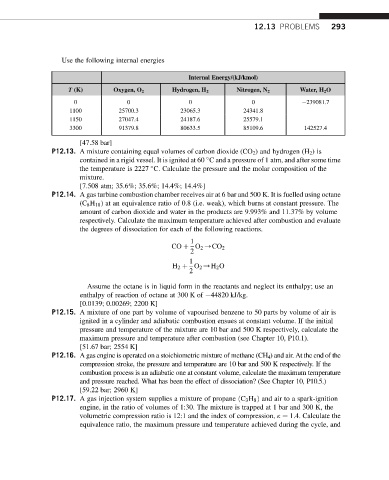
Use the following internal energies
Internal Energy/(kJ/kmol)
T (K) Oxygen, O 2 Hydrogen, H 2 Nitrogen, N 2 Water, H 2 O
0 0 0 0 239081.7
1100 25700.3 23065.3 24341.8
1150 27047.4 24187.6 25579.1
3300 91379.8 80633.5 85109.6 142527.4
[47.58 bar]
P12.13. A mixture containing equal volumes of carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and hydrogen (H 2 )is
contained in a rigid vessel. It is ignited at 60 C and a pressure of 1 atm, and after some time
the temperature is 2227 C. Calculate the pressure and the molar composition of the
mixture.
[7.508 atm; 35.6%; 35.6%; 14.4%; 14.4%]
P12.14. A gas turbine combustion chamber receives air at 6 bar and 500 K. It is fuelled using octane
(C 8 H 18 ) at an equivalence ratio of 0.8 (i.e. weak), which burns at constant pressure. The
amount of carbon dioxide and water in the products are 9.993% and 11.37% by volume
respectively. Calculate the maximum temperature achieved after combustion and evaluate
the degrees of dissociation for each of the following reactions.
1
CO þ O 2 /CO 2
2
1
H 2 þ O 2 /H 2 O
2
Assume the octane is in liquid form in the reactants and neglect its enthalpy; use an
enthalpy of reaction of octane at 300 K of 44820 kJ/kg.
[0.0139; 0.00269; 2200 K]
P12.15. A mixture of one part by volume of vapourised benzene to 50 parts by volume of air is
ignited in a cylinder and adiabatic combustion ensues at constant volume. If the initial
pressure and temperature of the mixture are 10 bar and 500 K respectively, calculate the
maximum pressure and temperature after combustion (see Chapter 10, P10.1).
[51.67 bar; 2554 K]
P12.16. A gas engine is operated on a stoichiometric mixture of methane (CH 4 ) and air. At the end of the
compression stroke, the pressure and temperature are 10 bar and 500 K respectively. If the
combustion process is an adiabatic one at constant volume, calculate the maximum temperature
and pressure reached. What has been the effect of dissociation? (See Chapter 10, P10.5.)
[59.22 bar; 2960 K]
P12.17. A gas injection system supplies a mixture of propane ðC 3 H 8 Þ and air to a spark-ignition
engine, in the ratio of volumes of 1:30. The mixture is trapped at 1 bar and 300 K, the
volumetric compression ratio is 12:1 and the index of compression, k ¼ 1.4. Calculate the
equivalence ratio, the maximum pressure and temperature achieved during the cycle, and