Page 426 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 426
416 CHAPTER 17 GAS TURBINES
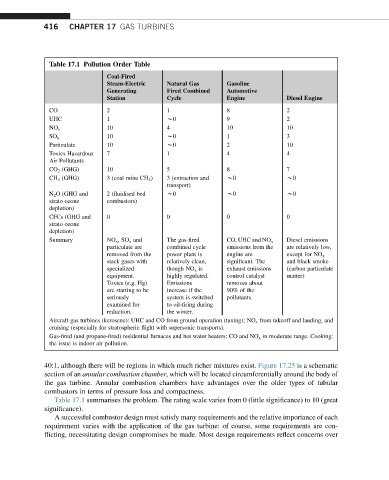
Table 17.1 Pollution Order Table
Coal-Fired
Steam-Electric Natural Gas Gasoline
Generating Fired Combined Automotive
Station Cycle Engine Diesel Engine
CO 2 1 8 2
UHC 1 w0 9 2
NO x 10 4 10 10
SO x 10 w0 1 3
Particulate 10 w0 2 10
Toxics Hazardous 7 1 4 4
Air Pollutants
CO 2 (GHG) 10 5 8 7
CH 4 (GHG) 3 (coal mine CH 4 ) 3 (extraction and w0 w0
transport)
N 2 O (GHG and 2 (fluidised bed w0 w0 w0
strato ozone combustors)
depletion)
CFCs (GHG and 0 0 0 0
strato ozone
depletion)
Summary NO x ,SO x and The gas-fired CO, UHC and NO x Diesel emissions
particulate are combined cycle emissions from the are relatively low,
removed from the power plant is engine are except for NO x
stack gases with relatively clean, significant. The and black smoke
specialized though NO x is exhaust emissions (carbon particulate
equipment. highly regulated. control catalyst matter)
Toxics (e.g. Hg) Emissions removes about
are starting to be increase if the 90% of the
seriously system is switched pollutants.
examined for to oil-firing during
reduction. the winter.
Aircraft gas turbines (kerosene): UHC and CO from ground operation (taxing); NO x from takeoff and landing, and
cruising (especially for stratospheric flight with supersonic transports).
Gas-fired (and propane-fired) residential furnaces and hot water heaters: CO and NO x in moderate range. Cooking:
the issue is indoor air pollution.
40:1, although there will be regions in which much richer mixtures exist. Figure 17.25 is a schematic
section of an annular combustion chamber, which will be located circumferentially around the body of
the gas turbine. Annular combustion chambers have advantages over the older types of tubular
combustors in terms of pressure loss and compactness.
Table 17.1 summarises the problem. The rating scale varies from 0 (little significance) to 10 (great
significance).
A successful combustor design must satisfy many requirements and the relative importance of each
requirement varies with the application of the gas turbine: of course, some requirements are con-
flicting, necessitating design compromises be made. Most design requirements reflect concerns over