Page 510 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 510
21.2 THEORY OF FUEL CELLS 503
Interconnection
Electrolyte
Air
Fuel flow
Electrode
Air
flow
Fuel
Porous electrode
support
tube
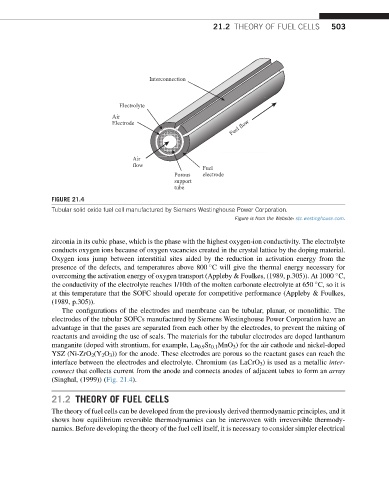
FIGURE 21.4
Tubular solid oxide fuel cell manufactured by Siemens Westinghouse Power Corporation.
Figure is from the Website: stc.westinghouse.com.
zirconia in its cubic phase, which is the phase with the highest oxygen-ion conductivity. The electrolyte
conducts oxygen ions because of oxygen vacancies created in the crystal lattice by the doping material.
Oxygen ions jump between interstitial sites aided by the reduction in activation energy from the
presence of the defects, and temperatures above 800 C will give the thermal energy necessary for
overcoming the activation energy of oxygen transport (Appleby & Foulkes, (1989, p.305)). At 1000 C,
the conductivity of the electrolyte reaches 1/10th of the molten carbonate electrolyte at 650 C, so it is
at this temperature that the SOFC should operate for competitive performance (Appleby & Foulkes,
(1989, p.305)).
The configurations of the electrodes and membrane can be tubular, planar, or monolithic. The
electrodes of the tubular SOFCs manufactured by Siemens Westinghouse Power Corporation have an
advantage in that the gases are separated from each other by the electrodes, to prevent the mixing of
reactants and avoiding the use of seals. The materials for the tubular electrodes are doped lanthanum
manganite (doped with strontium, for example, La 0.9 Sr 0.1 MnO 3 ) for the air cathode and nickel-doped
YSZ (Ni-ZrO 2 (Y 2 O 3 )) for the anode. These electrodes are porous so the reactant gases can reach the
interface between the electrodes and electrolyte. Chromium (as LaCrO 3 ) is used as a metallic inter-
connect that collects current from the anode and connects anodes of adjacent tubes to form an array
(Singhal, (1999)) (Fig. 21.4).
21.2 THEORY OF FUEL CELLS
The theory of fuel cells can be developed from the previously derived thermodynamic principles, and it
shows how equilibrium reversible thermodynamics can be interwoven with irreversible thermody-
namics. Before developing the theory of the fuel cell itself, it is necessary to consider simpler electrical