Page 506 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 506
21.1 TYPES OF FUEL CELLS 499
2e -
Oxidation at the anode Reduction at the cathode
H 2
CO
¼ CH 4
H O O 2- ½ O 2
2
CO 2
1/4
1/2 H O + CO 2
2
H 2
CO 2- ½ + CO
H O CO 3 O 2 2
+ CO 2
2
2CO 2
½ O 2
H 2 H +
H O
2
H 2
2OH - ½ O 2 + H O
2
2H O
2
1/3
1/3 CH OH + H O ½ O 2
3
2
2H +
1/3 CO 2 H O
2
½ O 2
H 2 H +
H O
2
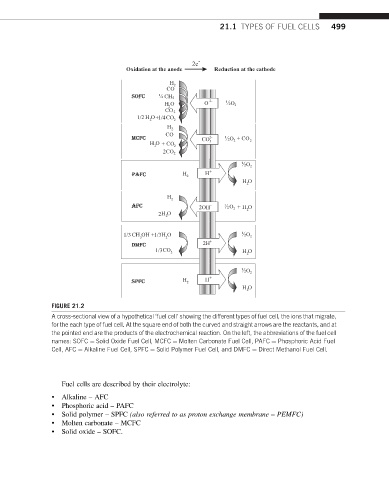
FIGURE 21.2
A cross-sectional view of a hypothetical ‘fuel cell’ showing the different types of fuel cell, the ions that migrate,
for the each type of fuel cell. At the square end of both the curved and straight arrows are the reactants, and at
the pointed end are the products of the electrochemical reaction. On the left, the abbreviations of the fuel cell
names: SOFC ¼ Solid Oxide Fuel Cell, MCFC ¼ Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell, PAFC ¼ Phosphoric Acid Fuel
Cell, AFC ¼ Alkaline Fuel Cell, SPFC ¼ Solid Polymer Fuel Cell, and DMFC ¼ Direct Methanol Fuel Cell.
Fuel cells are described by their electrolyte:
• Alkaline – AFC
• Phosphoric acid – PAFC
• Solid polymer – SPFC (also referred to as proton exchange membrane – PEMFC)
• Molten carbonate – MCFC
• Solid oxide – SOFC.